Blood culture time to positivity in pediatric patients with bloodstream infection in rural Gambia
- PMID: 40114912
- PMCID: PMC11923810
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijregi.2025.100606
Blood culture time to positivity in pediatric patients with bloodstream infection in rural Gambia
Abstract
Objectives: There is a lack of data on the time to blood culture positivity (TTP) in pediatric populations in low-income countries. We aimed to assess the host and pathogen factors associated with TTP in children aged under 5 years in rural Gambia.
Methods: Between September 2019 and December 2023, we collected blood cultures from children under 5 years with suspected bloodstream infections. We determined the TTP from the time of culture incubation to when bacterial growth was first detected.
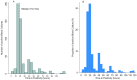
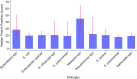
Results: Overall, 547 invasive bacteria pathogens were evaluated. The median TTP was 19.2 hours and 70%, 76%, 89%, and 96% of cases had TTP at 24, 36, 48, and 72 hours, respectively. Streptococcus pneumoniae had the shortest median TTP (17.4 hours), whereas Neisseria species had the longest (45 hours). TTP was dependent on the pathogen and independent of age, sex, temperature, clinical outcome, nutritional status, and length of hospital stay. Gram-positive bacteria had shorter TTP than gram-negative bacteria (18.6 vs 19.6 hours, P < 0.01).
Conclusions: In rural Gambia, most blood cultures from pediatric patients would turn positive within 48 hours of incubation. A maximum of 48 hours of observation after the commencement of antibiotic therapy in hospitalized children may be sufficient for clinicians to receive feedback on blood culture results.
Keywords: Blood cultures; Bloodstream infections; Children; The Gambia; Time-to-positivity.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Value of Time to Positivity of Blood Culture in Children with Bloodstream Infections.Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2019 Jan 10;2019:5975837. doi: 10.1155/2019/5975837. eCollection 2019. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30733846 Free PMC article.
-
Time to Positive Blood Cultures Among Critically Ill Children Admitted to the PICU.Crit Care Explor. 2024 Jul 5;6(7):e1115. doi: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000001115. eCollection 2024 Jul 1. Crit Care Explor. 2024. PMID: 38968174 Free PMC article.
-
Time to positivity of Klebsiella pneumoniae in blood culture as prognostic indicator for pediatric bloodstream infections.Eur J Pediatr. 2020 Nov;179(11):1689-1698. doi: 10.1007/s00431-020-03675-8. Epub 2020 May 11. Eur J Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32394266
-
Time to positivity of blood cultures supports antibiotic de-escalation at 48 hours.Ann Pharmacother. 2014 Jan;48(1):33-40. doi: 10.1177/1060028013511229. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Ann Pharmacother. 2014. PMID: 24259644
-
Time to positivity in blood cultures of adults with Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteremia.BMC Infect Dis. 2006 Apr 27;6:79. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-6-79. BMC Infect Dis. 2006. PMID: 16643662 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

