Ambroxol attenuates detrimental effect of LPS-induced glia-mediated neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and cognitive dysfunction in mice brain
- PMID: 40114925
- PMCID: PMC11923628
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1494114
Ambroxol attenuates detrimental effect of LPS-induced glia-mediated neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and cognitive dysfunction in mice brain
Abstract
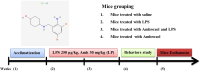
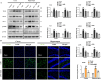
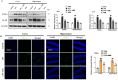
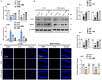
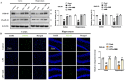
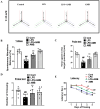
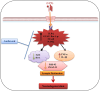
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD), are multifactorial. Among various factors, lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) from Gram-negative bacteria, such as E. coli, are considered potential causative agents. Despite significant advancements in the field, there is still no cure. In this study, we investigated the neuroprotective effects of ambroxol against LPS-induced neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, neurodegeneration, and the associated cognitive dysfunction. Intraperitoneal injection of LPS (250 µg/kg every alternative day for a total of seven doses over 14 days) triggered glial cell activation, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and neurodegeneration in the mouse brain. Ambroxol treatment (30 mg/kg/day for 14 days) significantly reduced neuroinflammation and oxidative stress compared to LPS-treated mice. Immunoblotting and immunofluorescence results showed that ambroxol reduced levels of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and oxidative stress kinase phospho-c-Jun N-terminal Kinase 1 (p-JNK). It also decreased astrocyte and microglia activation in the cortex and hippocampus of LPS+ Amb-treated mice, as indicated by the downregulation of GFAP and Iba-1. Furthermore, ambroxol-reversed LPS-induced neuroinflammation by inhibiting inflammatory mediators, such as IL-1β and TNF-α, through regulation of the transcription factor p-NFkB. Persistent neuroinflammation disrupted the natural antioxidant mechanisms, leading to oxidative stress. Ambroxol treatment upregulated antioxidant markers, including Nrf-2, HO-1, and SOD, which were downregulated in the LPS-treated group. Additionally, ambroxol-inhibited lipid peroxidation, maintaining malondialdehyde levels in the mouse brain. Ambroxol also improves synaptic integrity by upregulating synaptic biomarkers, including PSD-95 and SNAP-23. Overall, ambroxol demonstrated anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuroprotective effects in LPS-treated mice, highlighting its potential benefits in neurological disorders.
Keywords: ambroxol; cognitive; cognitive impairment; glial cells; lipopolysaccharide; neurodegeneration; neuroinflammation; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2025 Ullah, Park, Park, Atiq, Ali, Kang, Ali, Choe and Kim.
Conflict of interest statement
Author MOK was employed by the company Alz-Dementia Korea Co. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Patro I, et al. . General physiology and pathophysiology of microglia during neuroinflammation. In: Inflammation: the Common Link in Brain Pathologies (2016). p. 17–42.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

