Potential therapeutic mechanisms of Draconis Resina in cardiovascular diseases-a narrative review
- PMID: 40115265
- PMCID: PMC11922957
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1531873
Potential therapeutic mechanisms of Draconis Resina in cardiovascular diseases-a narrative review
Abstract
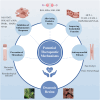
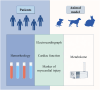
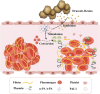
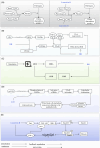
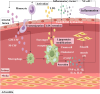
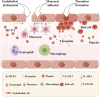
As a traditional Chinese herbal medicine, Draconis Resina (DR) has garnered significant attention due to its efficacy in treating various clinical diseases. Notably, it demonstrates remarkable therapeutic effects in cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, and myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. A comprehensive understanding of the potential therapeutic mechanisms of DR in cardiovascular diseases can positively influence their prevention and treatment. Therefore, through a thorough literature review, this paper summarizes the primary mechanisms of DR in managing cardiovascular diseases, which include the prevention of thrombosis, inhibition of inflammatory responses, alleviation of oxidative stress, enhancement of endothelial function, and mitigation of myocardial fibrosis. There may remain many untapped therapeutic applications of DR that need further exploration. This review aims to give readers a deeper understanding of the DR and offer new perspectives.
Keywords: cardioprotective effect; cardiovascular diseases; draconis resina; loureirin; pharmacology.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Tang, Lan, Liang, Fang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Bioactivity-Guided Fractionation of the Traditional Chinese Medicine Resina Draconis Reveals Loureirin B as a PAI-1 Inhibitor.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:9425963. doi: 10.1155/2017/9425963. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 29234445 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of microemulsion electrokinetic chromatography with high-performance liquid chromatography for fingerprint analysis of resina draconis.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2008 Nov;392(5):1003-10. doi: 10.1007/s00216-008-2337-9. Epub 2008 Aug 30. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2008. PMID: 18758761
-
[Simultaneous determination of five active components in resina draconis and its extract by HPLC].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2012 Apr;37(7):929-33. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22792791 Chinese.
-
The cardioprotective properties and the involved mechanisms of NaoXinTong Capsule.Pharmacol Res. 2019 Mar;141:409-417. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.01.024. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 30660824 Review.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine and mitophagy: A novel approach for cardiovascular disease management.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jun;128:155472. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155472. Epub 2024 Feb 24. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38461630 Review.
References
-
- Bao W., Wu H., Fang J. (2015). Clinical observation on 40 cases of acute myocardial infarction treated with western medical treatment and compound longxuejie capsules. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 56, 140–142. 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2015.02.014 - DOI
-
- Cheng C. (2017). To explore the protective effect of Dragon’s Blood on myocardial cells caused by ischemia-reperfusion injury in New Zealand rabbits based on the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Baise, Guangxi: Youjiang Medical College for Nationalities.
-
- Cheng C., Liang L., Liu Y., Li Z. (2017a). A study on protection effect of Resina Draconis on left ventricular function of acute myocardial infarction rabbits. Chin. Youjiang Med. J. 45, 15–19. 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1383.2017.01.004 - DOI
-
- Cheng C., Pan X., Liu W., Huang Z. (2017b). Study on the effect of total flavonoids of Dragon’s Blood on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in New Zealand rabbits. Cardio-Cerebrovasc. Dis. Prev. Treat. 17, 203–204+246. 10.3969/j.issn.1009-816x.2017.03.15 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

