The advancement and utility of multimodal imaging in the diagnosis of degenerative disc disease
- PMID: 40115420
- PMCID: PMC11922948
- DOI: 10.3389/fradi.2025.1298054
The advancement and utility of multimodal imaging in the diagnosis of degenerative disc disease
Abstract
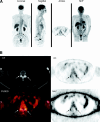
Degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a common spinal condition characterized by the deterioration of intervertebral discs, leading to chronic back pain and reduced mobility. While magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has long been the standard for late-stage DDD diagnosis, its limitations in early-stage detection prompt the exploration of advanced imaging methods. Positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) using 18F- fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) and 18F-sodium fluoride (NaF) has shown promise in identifying metabolic imbalances and age-related spinal degeneration, thereby complementing CT grading of the disease. The novel hybrid imaging modality PET/MRI provides new opportunities and are briefly discussed. The complex pathophysiology of DDD is dissected to highlight the role of genetic predisposition and lifestyle factors such as smoking and obesity. These etiological factors significantly impact the lumbosacral region, manifesting in chronic low back pain (LBP) and potential nerve compression. Traditional grading systems, like the Pfirrmann classification for MRI, are evaluated for their limitations in capturing the full spectrum of DDD. The potential to identify early disease processes and predict patient outcomes by the use of artificial intelligence (AI) is also briefly mentioned. Overall, the manuscript aims to spotlight advancements in imaging technologies for DDD, emphasizing their implications in refining both diagnosis and treatment strategies. The role of ongoing and future research is emphasized to validate these emerging techniques and overcome current limitations for more effective early detection and treatment.
Keywords: artificial intelligence (AI); degenerative disc disease (DDD); early diagnosis; imaging technologies; magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); pathophysiology; positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT); treatment strategies.
© 2025 Teichner, Subtirelu, Crutchfield, Parikh, Ashok, Talasila, Anderson, Patel, Mannam, Lee, Werner, Raynor, Alavi and Revheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Donnally III CJ, Hanna A, Varacallo M. Lumbar degenerative disk disease. StatPearls. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; (2023). http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448134/ (accessed August 31, 2023). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

