Diagnostic accuracy of interleukin-6 as a biomarker for early prediction of severe acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40115573
- PMCID: PMC11922355
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1366_24
Diagnostic accuracy of interleukin-6 as a biomarker for early prediction of severe acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Acute pancreatitis (AP) is an inflammatory disease of the pancreas with varying severity. The mortality rate varies from 20% to 40% among severe acute pancreatitis (SAP). Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine that involves various infections, inflammations, and systemic disorders. Injury to acinar cells leads to necrosis, releasing proinflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, which peaks earlier. The lack of extensive data regarding the association of IL-6 with AP influences us to do this meta-analysis for early detection and treatment of AP to prevent multiorgan failure.
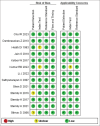
Methods: We searched the PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Google Scholar databases for relevant articles published from inception to June 2024. We examined the positive and negative likelihood ratios, diagnostic odds ratios, and pooled sensitivity and specificity. We used the QUADAS-2 tool to evaluate the risk of bias.
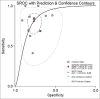
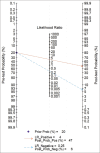
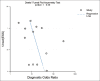
Results: This meta-analysis included 13 studies involving 1386 patients with AP, of which 343 had SAP and 1043 had mild and moderately severe AP. The positive and negative likelihood ratios were 3.5 (95% CI 2.6 to 4.5) and 0.25 (95% CI 0.16 to 0.40). The diagnostic odds ratio of IL-6 to diagnose SAP is 14 (95% CI: 7 to 27), and the summary receiver operating characteristic curve is 0.85 (95% CI: 0.82-0.88).
Conclusion: Based on the results of this meta-analysis, serum IL-6 is a promising biomarker for diagnosing SAP in the early stage. However, a larger-scale study involving a more extensive population is necessary due to the considerable variation between the studies.
Keywords: Acute pancreatitis; IL-6; diagnostic accuracy; sensitivity; specificity.
Copyright: © 2025 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Predictive value of the Ranson and BISAP scoring systems for the severity and prognosis of acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 30;19(4):e0302046. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302046. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38687745 Free PMC article.
-
Does the Automatic Measurement of Interleukin 6 Allow for Prediction of Complications during the First 48 h of Acute Pancreatitis?Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jun 20;19(6):1820. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061820. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29925813 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 in predicting severe acute pancreatitis: a meta-analysis.Pancreatology. 2009;9(6):777-85. doi: 10.1159/000214191. Epub 2010 Jan 21. Pancreatology. 2009. PMID: 20110745 Review.
-
[Construction of prediction model of severe acute pancreatitis based on serum soluble T cell immunogloblulin and mucin domain-containing protein 3].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Jan;36(1):67-72. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20230128-00041. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 38404275 Chinese.
-
Accuracy of angiopoietin-2 for predicting organ failure in patients with acute pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Int Med Res. 2021 Feb;49(2):300060520986708. doi: 10.1177/0300060520986708. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33527867 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Phospholipase D2: A biomarker implicated in various pancreatic diseases beyond acute pancreatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 Jul 28;31(28):108271. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i28.108271. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40741474 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Interleukin-6 Mediated T Cell Activation in Experimental Acute Pancreatitis.Inflammation. 2025 Jun 25. doi: 10.1007/s10753-025-02329-x. Online ahead of print. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 40560328 No abstract available.
References
-
- Schepers NJ, Bakker OJ, Besselink MG, Ahmed Ali U, Bollen TL, Gooszen HG, et al. Impact of characteristics of organ failure and infected necrosis on mortality in necrotizing pancreatitis. Gut. 2019;68:1044–51. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal S, George J, Padhan RK, Vadiraja PK, Behera S, Hasan A, et al. Reduction in mortality in severe acute pancreatitis: A time trend analysis over 16 years. Pancreatology. 2016;16:194–9. - PubMed
-
- Ranson JH, Rifkind KM, Roses DF, Fink SD, Eng K, Spencer FC. Prognostic signs and the role of operative management in acute pancreatitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1974;139:69–81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
