Real-world effectiveness and safety of TACE combined with lenvatinib plus immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with BCLC-B stage hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 40115929
- PMCID: PMC11921401
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-2025-33
Real-world effectiveness and safety of TACE combined with lenvatinib plus immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with BCLC-B stage hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: More effective treatment strategies need to be established for patients with Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC)-B stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The combination of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) with lenvatinib and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) has been shown to have potential in the treatment of unresectable HCC. However, the real-world data on the use of this combined therapy in patients with BCLC-B stage HCC are limited. Therefore, this study aimed to validate the efficacy and safety of the combination of TACE with lenvatinib plus ICIs in the treatment of patients with BCLC-B stage HCC in a real-world setting.
Methods: A total of 121 patients who were newly diagnosed with BCLC-B stage HCC were enrolled in this study. Of these patients, 52 received treatment with TACE combined with lenvatinib plus ICIs (the combination group), and 69 received TACE alone (the monotherapy group). Propensity score matching (PSM) was used to reduce potential biases. The primary endpoint of the study was overall survival (OS), while the secondary endpoints were progression-free survival (PFS), the objective response rate (ORR), and the disease control rate (DCR). Adverse events (AEs) were also recorded and evaluated.
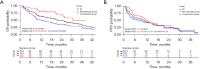
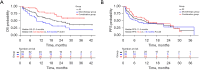
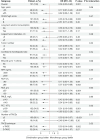
Results: The OS of the combination group was longer than that of the monotherapy group (median OS: 30.9 vs. 13.0 months, P<0.001), as was the PFS (median PFS: 12.3 vs. 8.3 months, P=0.19). The ORR of the combination group was higher than that of the monotherapy group (61.5% vs. 33.3%, P=0.002), as was the DCR (92.3% vs. 76.8%, P=0.02). After PSM, the OS of the combination group was longer than that of the monotherapy group (median OS: not reached vs. 9.8 months, P<0.001), as was the PFS (median PFS: 13.4 vs. 7.6 months, P=0.28). The ORR of the combination group was higher than that of the monotherapy group (59.0% vs. 30.8%, P=0.01), as was the DCR (89.7% vs. 74.4%, P=0.08). In the multivariate Cox regression analysis, combination therapy was associated with a better OS (hazard ratio =0.36, 95% confidence interval: 0.20-0.64, P<0.001). In terms of the AEs, 8 of 52 patients (15.4%) in the combination group, and 4 of 69 patients (5.8%) in the monotherapy group experienced grade 3 or 4 AEs (P=0.08), but no grade 5 AEs were observed.
Conclusions: The combination of TACE with lenvatinib plus ICIs showed excellent efficacy in the treatment of patients with BCLC-B stage HCC, and the safety profile was acceptable.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs); lenvatinib; overall survival (OS); transarterial chemoembolization (TACE).
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jgo.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jgo-2025-33/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Combined with Lenvatinib versus TACE Alone in Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Beyond Up-To-Seven Criteria: A Retrospective, Propensity Score-Matched Analysis.Acad Radiol. 2024 Nov;31(11):4456-4465. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2024.04.045. Epub 2024 May 17. Acad Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38760273
-
Transarterial chemoembolization combined with molecular targeted agents plus immune checkpoint inhibitors for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the up-to-seven criteria: a propensity score-matching analysis.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2419993. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2419993. Epub 2024 Nov 1. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 39484705 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization combined with lenvatinib and camrelizumab in patients with BCLC-defined stage C hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Oct 17;13:1244341. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1244341. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37916160 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy improved the efficacy of TACE or TACE plus MTTs in HCC patients: A meta-analysis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Feb 6;147:114006. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.114006. Epub 2025 Jan 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39793227 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization plus lenvatinib combined with PD-1 inhibitors versus transarterial chemoembolization plus lenvatinib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 30;15:1466113. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1466113. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39281676 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
