Epidemiology of Staphylococcus haemolyticus nosocomial bacteraemia in neonatal intensive care units, France, 2019 to 2023: predominance of the ST29 (CC3) multidrug-resistant lineage
- PMID: 40116031
- PMCID: PMC11927072
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.11.2400309
Epidemiology of Staphylococcus haemolyticus nosocomial bacteraemia in neonatal intensive care units, France, 2019 to 2023: predominance of the ST29 (CC3) multidrug-resistant lineage
Abstract
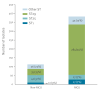
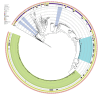
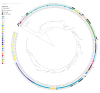
BackgroundStaphylococcus haemolyticus (SH) is an opportunistic pathogen associated with nosocomial infections, particularly bacteraemia in neonates. Epidemiological trends and genetic diversity of these infections worldwide are largely unknown.AimTo investigate an increase in SH vascular catheter-related bacteraemia in neonates and describe the molecular epidemiology in France between 2019 and 2023.MethodsWe analysed clinical and microbiological surveillance data from the French national surveillance network for central catheter-related (venous and umbilical) infections between 2019 and 2023. We also performed genomic and phylogenetic analyses of 496 strains isolated both inside (n = 383 from neonates, staff and environmental samples) and outside (n = 113 from adults) the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) settings.ResultsThe proportion of SH among the 474 reported cases of nosocomial bacteraemia increased from about 20% to 30% over 5 years, mainly affecting very low birth weight preterm neonates (≤ 1,500 g). The ST29 sequence type (ST) not prevalent in previous studies was predominant, accounting for 74% of NICU strains. ST29 was characterised by phenotypic multidrug resistance to at least six classes of antibiotics (oxacillin, quinolones, gentamicin, cotrimoxazole, clindamycin and rifampicin), which distinguished it with good sensitivity and specificity from other prevalent multidrug-resistant STs identified (ST1 and ST25). ST29 strains more frequently harboured the drfG, vga-LC and mupA genes and a triple point mutation (D471E, I527M and S532N) in the rpoB gene.ConclusionsThe present study highlights the success of a highly resistant ST29 lineage in French NICUs mainly affecting very low birth weight premature neonates.
Keywords: Staphylococcus haemolyticus; bacteraemia; bloodstream infections; epidemiology; multi-drug resistance; neonatal infections; neonatal intensive care units; outbreak.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Klingenberg C, Rønnestad A, Anderson AS, Abrahamsen TG, Zorman J, Villaruz A, et al. Persistent strains of coagulase-negative staphylococci in a neonatal intensive care unit: virulence factors and invasiveness. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007;13(11):1100-11. 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01818.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jaloustre M, Cohen R, Biran V, Decobert F, Layese R, Audureau E, et al. Determinants of morbidity and mortality related to health care-associated primary bloodstream infections in neonatal intensive care units: a prospective cohort study from the SEPREVEN trial. Front Pediatr. 2023;11:1170863. 10.3389/fped.2023.1170863 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
