Surgical Site Infections, Risk Factors, and Outcomes After Liver Transplant
- PMID: 40116828
- PMCID: PMC11929024
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.1333
Surgical Site Infections, Risk Factors, and Outcomes After Liver Transplant
Abstract
Importance: Surgical site infections (SSIs) are one of the most common health care-associated infections. Surgical site infections can have harmful effects in liver transplant (LT) recipients.
Objective: To assess the incidence of SSI after LT and identify risk factors associated with SSIs and whether SSIs are associated with death and graft loss.
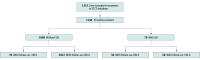
Design, setting, and participants: A multicenter cohort study encompassing data on LT performed at all Swiss transplant centers between May 1, 2008, and September 30, 2020, was conducted. Data analyses were performed in 2023.
Exposure: Liver transplant.
Main outcomes and measures: Frequency of SSIs within 90 days after transplant, risk factors associated with SSIs, and association of SSIs with 1-year death or graft loss. Surgical site infections were defined according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention criteria with SSIs occurring within 90 days after LT. For association with posttransplant outcomes, 1-year follow-up data were analyzed.
Results: Among 1333 LT recipients in the Swiss Transplant Cohort Study, 1158 adults were included in analyses. Median age was 57.2 (IQR, 49.3-62.8) years and 792 were men (68.4%). Seventy patients (6.0%) had an SSI. Most SSIs were deep incisional (9 [12.8%]) or organ-space infections (54 [77.1%]). In most SSIs (56 [80.0%]), bacteria were detected, most frequently Enterococcus spp (36 of 75 [48.0%]) and Escherichia coli (12 of 75 [16.0%]). In multivariable analysis, prior liver transplant (odds ratio [OR] 4.01; 95% CI, 1.44-11.18; P = .008) and living liver donation (OR, 4.08; 95% CI, 1.37-12.16; P = .01) were independent risk factors associated with SSIs. Surgical site infections were independently associated with graft loss and/or death (hazard ratio [HR], 3.24; 95% CI, 1.82-5.79; P < .001); this association was observed in separate analyses on graft loss (HR, 2.97; 95% CI, 1.32-6.68; P = .02) and death (HR, 3.25; 95% CI, 1.44-7.35; P = .01).
Conclusions and relevance: The findings of this study suggest that prior liver transplant and living liver donation are independent risk factors associated with SSIs and that SSIs are independently associated with graft loss and/or death, highlighting the relevance of this health care-associated infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
References
-
- Bundesamt für Gesundheit. Zahlen zur Spende und Transplantation von Organen in der Schweiz. Accessed month day, year. https://www.bag.admin.ch/bag/de/home/zahlen-und-statistiken/zahlen-fakte...
-
- Magill SS, Edwards JR, Bamberg W, et al. ; Emerging Infections Program Healthcare-Associated Infections and Antimicrobial Use Prevalence Survey Team . Multistate point-prevalence survey of health care–associated infections. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(13):1198-1208. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1306801 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

