Age-dependent cytokine surge in blood precedes cancer diagnosis
- PMID: 40117305
- PMCID: PMC11962427
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2420502122
Age-dependent cytokine surge in blood precedes cancer diagnosis
Abstract
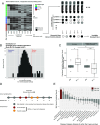
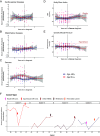
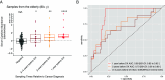
Aging is associated with increased variability and dysregulation of the immune system. We performed a system-level analysis of serum cytokines in a longitudinal cohort of 133 healthy individuals over 9 y. We found that cancer incidence is a major contributor to increased cytokine abundance variability. Circulating cytokines increase up to 4 y before a cancer diagnosis in subjects with age over 80 y. We also analyzed cytokine expression in 10 types of early-stage cancers from The Cancer Genome Atlas. We found that a similar set of cytokines is upregulated in tumor tissues, specifically after the age of 80 y. Similarly, cellular senescence activity and CDKN1A/p21 expression increase with age in cancer tissues. Finally, we demonstrated that the cytokine levels in serum can be used to predict cancers among subjects age at 80+ y. Our results suggest that latent senescent cancers contribute to age-related chronic inflammation.
Keywords: aging; cancer; cytokine surge; immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures



References
-
- Franceschi C., Garagnani P., Parini P., Giuliani C., Santoro A., Inflammaging: A new immune–metabolic viewpoint for age-related diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 14, 576–590 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Franceschi C., Campisi J., Chronic inflammation (Inflammaging) and its potential contribution to age-associated diseases. J. Gerontol.: Series A 69, S4–S9 (2014). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

