GM-CSF-mediated epithelial-immune cell cross-talk orchestrates pulmonary immunity to Aspergillus fumigatus
- PMID: 40117345
- PMCID: PMC12122100
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.adr0547
GM-CSF-mediated epithelial-immune cell cross-talk orchestrates pulmonary immunity to Aspergillus fumigatus
Abstract
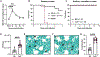
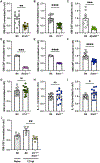
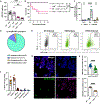
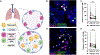
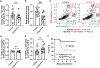
Aspergillus fumigatus causes life-threatening mold pneumonia in immunocompromised patients, particularly in those with quantitative or qualitative defects in neutrophils. Whereas innate immune cell cross-talk licenses neutrophil antifungal activity in the lung, the role of epithelial cells in this process is unknown. Here, we find that surfactant protein C (SPC)-expressing lung epithelial cells integrate infection-induced interleukin-1 and type III interferon signaling to produce granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) preferentially at local sites of fungal infection and neutrophil influx. Using in vivo models that distinguish the role of GM-CSF during acute infection from its homeostatic function in alveolar macrophage survival and surfactant catabolism, we demonstrate that epithelial-derived GM-CSF increases the accumulation and fungicidal activity of GM-CSF-responsive neutrophils, which is essential for host survival. Our findings establish SPC+ epithelial cells as a central player in regulating the quality and strength of neutrophil-dependent immunity against inhaled mold pathogens.
Figures
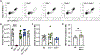
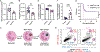
Update of
-
GM-CSF-mediated epithelial-immune cell crosstalk orchestrates pulmonary immunity to Aspergillus fumigatus.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 4:2024.01.03.574062. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.03.574062. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Sci Immunol. 2025 Mar 21;10(105):eadr0547. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.adr0547. PMID: 38260364 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Guo Y, Kasahara S, Jhingran A, Tosini NL, Zhai B, Aufiero MA, Mills KAM, Gjonbalaj M, Espinosa V, Rivera A, Luster AD, Hohl TM, During Aspergillus infection, monocyte-derived DCs, neutrophils, and plasmacytoid DCs enhance innate immune defense through CXCR3-dependent crosstalk. Cell Host Microbe 28, 104–116.e4 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gerson SL, Talbot GH, Hurwitz S, Strom BL, Lusk EJ, Cassileth PA, Prolonged granulocytopenia: The major risk factor for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with acute leukemia. Ann. Intern. Med 100, 345–351 (1984). - PubMed
-
- Nivoix Y, Velten M, Letscher-Bru V, Moghaddam A, Natarajan-Amé S, Fohrer C, Lioure B, Bilger K, Lutun P, Marcellin L, Launoy A, Freys G, Bergerat J, Herbrecht R, Factors associated with overall and attributable mortality in invasive aspergillosis. Clin. Infect. Dis 47, 1176–1184 (2008). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

