Genomic Characterization of Chondrosarcoma Reveals Potential Therapeutic Targets
- PMID: 40117529
- PMCID: PMC11949235
- DOI: 10.1200/PO-24-00592
Genomic Characterization of Chondrosarcoma Reveals Potential Therapeutic Targets
Abstract
Purpose: Chondrosarcomas are rare cancers of cartilage with limited systemic therapy options. To identify potential therapeutic targets, this study investigated the molecular and immune landscape of three chondrosarcoma subtypes using a large database of clinical-grade sequencing results.
Methods: Deidentified records from patients with a histologic diagnosis of conventional, dedifferentiated, or mesenchymal chondrosarcoma sequenced by the Tempus xT DNA assay were included. Microsatellite instability (MSI) and tumor mutational burden (TMB) were determined from sequencing data. The expression of PD-L1 and mismatch repair enzymes was evaluated in cases with available immunohistochemistry (IHC) data.
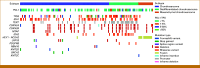
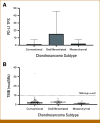
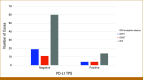
Results: Of the 149 patients, 103 had conventional chondrosarcoma, 31 dedifferentiated chondrosarcoma, and 15 mesenchymal chondrosarcoma. Across the cohort, 44% (n = 65) had an IDH1 or IDH2 mutation. No cases were MSI high. One conventional chondrosarcoma patient had a TMB >10 mut/Mb. Among 112 patients with available PD-L1 IHC, 10% of conventional (n = 7), 45% of dedifferentiated (n = 13), and 17% of mesenchymal cases (n = 2) were PD-L1-positive. The most common somatic alterations were in IDH1 (34%) and TP53 (28%) in conventional chondrosarcoma; TP53 (68%), TERT (65%), IDH1 (39%), IDH2 (39%), CDKN2A (35%), and CDKN2B (35%) in dedifferentiated chondrosarcoma; and HEY1-NCOA2 fusions (87%) and CDKN2A (20%) in mesenchymal chondrosarcoma. MTAP was deleted in >10% of each subtype, and potentially actionable PDGFRB mutations were identified in 13% of dedifferentiated chondrosarcomas.
Conclusion: These findings reinforce therapeutic efforts to target IDH signaling in chondrosarcoma, provide insight into varied subpopulation response to immune checkpoint inhibitors, and identify new potential therapeutic targets for clinical development in chondrosarcoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures
References
-
- Hompland I, Ferrari S, Bielack S, et al. : Outcome in dedifferentiated chondrosarcoma for patients treated with multimodal therapy: Results from the EUROpean Bone Over 40 Sarcoma Study. Eur J Cancer 151:150-158, 2021 - PubMed
-
- Wagner MJ, Livingston JA, Patel SR, et al. : Chemotherapy for bone sarcoma in adults. JCO Oncol Pract 12:208-216, 2016 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

