Treatment Advances in Vitiligo: An Updated Review
- PMID: 40117616
- PMCID: PMC11928143
- DOI: 10.5826/dpc.1501a4600
Treatment Advances in Vitiligo: An Updated Review
Abstract
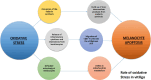
Introduction: Vitiligo is a common disorder of depigmentation caused by the progressive destruction of melanocytes that affects the skin, hair, and mucous membranes, clinically presenting as depigmented macules and leukotrichia. This condition, affecting millions of people worldwide, has a significant psychosocial burden on patients' quality of life, particularly in relation to skin colour. The etiopathogenesis of this disorder is obscure, but multiple factors contribute to the loss of melanocytes in the skin, like oxidative stress, inflammation, genetics, and autoimmunity. The treatment of vitiligo has been challenging over the past years, but recent developments in understanding the etiopathogenesis of the disease have paved the way for the development of more effective and promising therapeutic treatment options.
Objective: The aim of this review was to provide an overview of the underlying mechanisms and highlight the latest advances in the treatment of vitiligo.
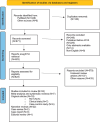
Methodology: This review was performed according to PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Metanalyses) guidelines. A comprehensive search of the literature was carried out through the PubMed electronic database from inception to 31 December 2023 using the following search terms "vitiligo" AND "JAK inhibitors", "vitiligo" AND "prostaglandin", " vitiligo" AND " afamelanotide", "vitiligo" AND "antioxidants", "vitiligo" AND "vitamin D3", "vitiligo" AND "statins", "vitiligo" AND "TNF-alpha", "vitiligo" AND "interleukin", "vitiligo" AND "light therapy". Two independent reviewers screened titles, abstracts, and full texts to select papers dealing with vitiligo and its treatment.
Conclusion: The advent of treatment modalities like Janus kinase inhibitors, prostaglandin analogues, antioxidants, TNF-α inhibitors, targeted phototherapy, and excimer lasers has revolutionized the therapeutic possibilities, offering a ray of hope to the individuals suffering from this devastating condition.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The use of Janus kinase inhibitors and narrowband ultraviolet B combination therapy in non-segmental vitiligo.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2023 Mar;22(3):1105-1107. doi: 10.1111/jocd.15537. Epub 2022 Nov 28. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 36440703
-
Repigmentation in vitiligo using janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors with phototherapy: systematic review and Meta-analysis.J Dermatolog Treat. 2022 Feb;33(1):173-177. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2020.1735615. Epub 2020 Apr 2. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022. PMID: 32096671
-
Vitiligo, from Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Advances: State of the Art.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 3;24(5):4910. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054910. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JAK inhibitors in immune regulation and treatment of vitiligo.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2024 Dec;80:87-96. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2024.11.002. Epub 2024 Nov 10. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2024. PMID: 39567266 Review.
-
Biologic and targeted therapeutics in vitiligo.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2023 Jan;22(1):64-73. doi: 10.1111/jocd.14770. Epub 2022 Feb 9. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 35029034 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipidome Complexity in Physiological and Pathological Skin Pigmentation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 15;26(14):6785. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146785. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Injectable crosslinked HA hydrogel: a promising carrier for cell transplantation to treat stable vitiligo.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 May 12;12:1583271. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1583271. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40421296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iwanowski T, Szlązak P, Zabłotna M, Olszewska B, Sokołowska-Wojdyło M. Translation, cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the vitiligo-specific health-related quality of life instrument (VitiQoL) into Polish. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2021;38(4):636–643. doi: 10.5114/ada.2021.108896. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ezzedine K, Lim HW, Suzuki T, et al. Vitiligo Global Issue Consensus Conference Panelists. Revised classification/nomenclature of vitiligo and related issues: the Vitiligo Global Issues Consensus Conference. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012;25(3):E1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-148X.2012.00997.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous