Retrospective cohort study assessing clinical outcomes of patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer treated with and without consolidative thoracic radiotherapy at the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre
- PMID: 40118489
- PMCID: PMC11931945
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-093943
Retrospective cohort study assessing clinical outcomes of patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer treated with and without consolidative thoracic radiotherapy at the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre
Abstract
Objectives: Most patients with small cell lung cancer present with extensive-stage (ES-SCLC) disease. An international randomised trial demonstrated a survival benefit in patients treated with consolidative thoracic radiotherapy (cTRT). We report our institutional experience with this regimen.
Methods: A retrospective review was conducted on patients with ES-SCLC who were candidates for cTRT at our institution between 2013 and 2022. The patients included in our study had biopsy-proven ES-SCLC, received ≥4 cycles of chemotherapy and achieved complete response, partial response or stable disease as per Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors V.1.1. Overall survival, progression-free survival (PFS) and recurrence patterns were compared between patients who received cTRT and those who did not. For patients who received cTRT, treatment tolerability was assessed.
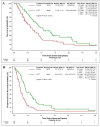
Results: We identified 123 patients with ES-SCLC who received ≥4 cycles of chemotherapy and were candidates for cTRT. Of those, 49 patients received cTRT, and 74 patients did not. From the end of chemotherapy, the control group had a median OS of 0.6 years with a 1- and 2-year OS of 23.5% and 11.0%. Within the cTRT group, the median OS was 0.9 years with a 1- and 2-year OS of 46.7% and 26.3%. Within the control group, the median PFS was 0.2 years compared with 0.4 years within the cTRT group. Intrathoracic failures in the cTRT group were lower compared with the control group (16.3% vs 29.7%). cTRT was well tolerated with no grade 3+ toxicities.
Conclusion: The improved clinical outcomes of cTRT for patients with ES-SCLC were comparable to the reported the Chest Radiotherapy Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer Trial (CREST) outcome, with a low rate of side effects in our study cohort.
Keywords: Lung Diseases; ONCOLOGY; Radiation oncology.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: VS, RS, HL, XY and LZ: no conflict of interest. AS: honoraria and advisory committee member for AstraZeneca and Merck. Unrelated to this study. AB: advisory committee for AstraZeneca and AbbVie. Unrelated to this study. JC: advisory committee for Canadian Mesothelioma Foundation. Unrelated to this study. SR: institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Knight therapeutics. Honoraria from Bayer, AstraZeneca, Tersera, Sanofi and Verity Pharma. Unrelated to this study. AH: indirect support from AstraZeneca and Elekta. Unrelated to this study. MG: advisory committee for AstraZeneca and Bristol-Myers Squibb. Unrelated to this study. NBL: institutional research funding from Amgen, AstraZeneca Canada, Bayer, EMD Serono, Guardant Health, Eli Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme Oncology, Roche Canada and Takeda. Travel funding from Merck Sharp & Dohme. Unrelated to this study. AGS: institutional research funding from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CRISPR Therapeutics AG, Eli Lilly, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Iovance, Merck, Pfizer and Spectrum Pharmaceuticals. Advisory board member for AstraZeneca and Genentech. Unrelated to this study. FS: institutional research funding from Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Roche Canada, Merrimack. Honoraria from Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Merck Serono, Boehringer Ingelheim. Advisory board for Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim and Merck Serono. Stock in Eli Lilly and AstraZeneca. Unrelated to this study. PAB: honoraria from Merck, Pfizer and Eli Lilly. Advisory committee for Abbvie, Mirati, AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim. Unrelated to this study. GL: institutional research funding from NCI (US), CIHR (Canada), CCSRI (Canada), Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim and Takeda. Honoraria from AstraZeneca, EMD Serono, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Pfizer and Takeda. Advisory committee for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BMS, EMD Serono, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and Takeda. Unrelated to this study. BK: institutional research funding from Pfizer. Grants, personal fees and non-financial support from AstraZeneca. Personal fees from Daiichi-Sankyo. Unrelated to this study.
Figures

References
-
- American Cancer Society Cancer Facts & Statistics. http://cancerstatisticscenter.cancer.org/ Available.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
