Polygenic Risk and Cardiovascular Event Risk in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation With Low to Intermediate Stroke Risk
- PMID: 40118812
- PMCID: PMC12132817
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.124.037727
Polygenic Risk and Cardiovascular Event Risk in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation With Low to Intermediate Stroke Risk
Abstract
Background: The clinical utility of the polygenic risk score in predicting cardiovascular events in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) has not yet been established. This study aimed to determine whether the polygenic risk score for AF might be useful in the risk stratification of AF-related cardiovascular events.
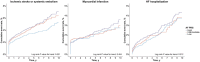
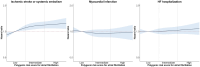
Methods and results: This study included 9597 oral anticoagulation-naive patients with AF with a CHA2DS2-VA (congestive heart failure; hypertension; age ≥75 years; diabetes; prior stroke or transient ischemic attack or thromboembolism; vascular disease; and age 65-74 years) score of 0 or 1 from the UK Biobank. Patients were stratified according to polygenic risk score tertiles and observed for the occurrence of ischemic stroke or systemic embolism, myocardial infarction, and heart failure hospitalization. The risks of incident events associated with the polygenic risk score were investigated using inverse probability of treatment weighting. Of 9597 individuals, 3800 (39.6%) were women and the mean±SD age was 65.3±6.4 years. During a median follow-up of 4.6 years (interquartile range, 1.7-7.9 years), the incidence rates of ischemic stroke or systemic embolism, myocardial infarction, and heart failure hospitalization were 0.83, 0.42, and 0.61 per 100 person-years, respectively. Compared with low genetic risk, high genetic risk was associated with a hazard ratio of 1.38 (95% CI, 1.08-1.76; P=0.011) for ischemic stroke or systemic embolism, 1.15 (95% CI, 0.82-1.61; P=0.422) for myocardial infarction, and 1.02 (95% CI, 0.78-1.34; P=0.895) for heart failure hospitalization.
Conclusions: In patients with AF with low-intermediate stroke risk, genetic risk for AF is associated with increased risk of stroke or systemic embolism.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; polygenic risk score; stroke risk.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Joung has served as a speaker for Bayer, BMS/Pfizer, Medtronic, and Daiichi‐Sankyo and has received research funds from Medtronic and Abbott. No fees were received, either directly or personally. The remaining authors have no other relationships or activities that could have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Hijazi Z, Lindback J, Alexander JH, Hanna M, Held C, Hylek EM, Lopes RD, Oldgren J, Siegbahn A, Stewart RA, et al. The ABC (age, biomarkers, clinical history) stroke risk score: a biomarker‐based risk score for predicting stroke in atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 2016;37:1582–1590. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw054 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lip GY, Nieuwlaat R, Pisters R, Lane DA, Crijns HJ. Refining clinical risk stratification for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation using a novel risk factor‐based approach: the euro heart survey on atrial fibrillation. Chest. 2010;137:263–272. doi: 10.1378/chest.09-1584 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Piccini JP, Stevens SR, Chang Y, Singer DE, Lokhnygina Y, Go AS, Patel MR, Mahaffey KW, Halperin JL, Breithardt G, et al. Renal dysfunction as a predictor of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2013;127:224–232. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.107128 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

