Identification of PTGR2 inhibitors as a new therapeutic strategy for diabetes and obesity
- PMID: 40119175
- PMCID: PMC12081876
- DOI: 10.1038/s44321-025-00216-4
Identification of PTGR2 inhibitors as a new therapeutic strategy for diabetes and obesity
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Identification of PTGR2 inhibitors as a new therapeutic strategy for diabetes and obesity.EMBO Mol Med. 2025 May;17(5):1184. doi: 10.1038/s44321-025-00228-0. EMBO Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40181187 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
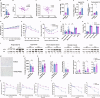
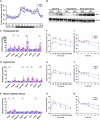
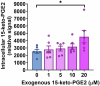
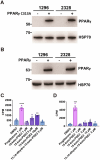
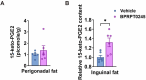
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) is a master transcriptional regulator of systemic insulin sensitivity and energy balance. The anti-diabetic drug thiazolidinediones (TZDs) are potent synthetic PPARγ ligands with undesirable side effects, including obesity, fluid retention, and osteoporosis. 15-keto prostaglandin E2 (15-keto-PGE2) is an endogenous PPARγ ligand metabolized by prostaglandin reductase 2 (PTGR2). Here, we confirmed that 15-keto-PGE2 binds to and activates PPARγ via covalent binding. In patients with type 2 diabetes and obese mice, serum 15-keto-PGE2 levels were decreased. Administration of 15-keto-PGE2 improves glucose homeostasis and prevented diet-induced obesity in mice. Either genetic inhibition of PTGR2 or PTGR2 inhibitor BPRPT0245 protected mice from diet-induced obesity, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis without causing fluid retention and osteoporosis. In conclusion, inhibition of PTGR2 is a new therapeutic approach to treat diabetes and obesity through increasing endogenous PPARγ ligands while avoiding side effects including increased adiposity, fluid retention, and osteoporosis.
Keywords: 15-keto-PGE2; Diabetes; Obesity; PPARγ; PTGR2.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Ardenkjær-Skinnerup J, Saar D, Petersen PSS, Pedersen M, Svingen T, Kragelund BB, Hadrup N, Ravn-Haren G, Emanuelli B, Brown KA et al (2024) PPARγ antagonists induce aromatase transcription in adipose tissue cultures. Biochem Pharmacol 222:116095 - PubMed
-
- Bruning JB, Chalmers MJ, Prasad S, Busby SA, Kamenecka TM, He Y, Nettles KW, Griffin PR (2007) Partial agonists activate PPARgamma using a helix 12 independent mechanism. Structure 15(10):1258–1271 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

