MEOX2 mediates cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer via E2F target and DNA repair pathways
- PMID: 40119426
- PMCID: PMC11927352
- DOI: 10.1186/s13048-025-01641-2
MEOX2 mediates cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer via E2F target and DNA repair pathways
Abstract
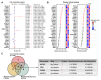
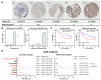
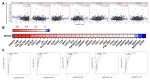
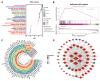
Ovarian cancer (OV) is a leading cause of cancer-related mortality among women worldwide. Despite the success of platinum-based chemotherapy in treating OV, the emergence of cisplatin resistance has significantly compromised its therapeutic efficacy. Therefore, understanding the mechanisms underlying cisplatin resistance and its molecular regulation is crucial for improving patient outcomes. This study, MEOX2 was identified as a key gene significantly associated with prognosis and cisplatin resistance in OV through bioinformatics analysis. Its expression level and biological functions were validated using online databases, tissue microarrays, and cellular experiments. The results demonstrated that high MEOX2 expression was closely associated with poor survival outcomes in OV patients, while its expression was significantly reduced in cisplatin-resistant cells. Further gene silencing experiments revealed that silencing MEOX2 markedly enhanced cisplatin resistance in resistant cells and significantly reduced cisplatin-induced early apoptosis, although it had no notable effect on cell proliferation. Moreover, the study showed that MEOX2 was not associated with immune cell infiltration in OV but was positively correlated with angiogenesis-related genes. In cisplatin-resistant cells, gene set enrichment analysis of MEOX2 co-expressed genes highlighted the activation of the E2F target and DNA repair pathway. Additionally, MEOX2 exhibited a significant negative correlation with the MCM protein family. In summary, MEOX2 is highly expressed in OV and is associated with poor patient prognosis. It may confer cisplatin resistance to OV cells by activating the E2F target and DNA repair pathway to mitigate cisplatin-induced early apoptosis. Despite certain limitations, these findings provide novel insights into the potential role of MEOX2 as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in OV.
Keywords: Cisplatin resistance; MEOX2; Ovarian cancer; Prognosis; Transcriptomic analysis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Institutional review board statement: Not applicable. Informed consent: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
HOXB2 promotes cisplatin resistance by upregulating lncRNA DANCR in ovarian cancer.J Ovarian Res. 2024 Jun 8;17(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s13048-024-01424-1. J Ovarian Res. 2024. PMID: 38851728 Free PMC article.
-
TNFRSF10D expression as a potential biomarker for cisplatin-induced damage and ovarian tumor relapse prediction.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Nov;263:155592. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155592. Epub 2024 Sep 7. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 39255671
-
HIF-2α-dependent TGFBI promotes ovarian cancer chemoresistance by activating PI3K/Akt pathway to inhibit apoptosis and facilitate DNA repair process.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 16;14(1):3870. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53854-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38365849 Free PMC article.
-
ARL6IP5 reduces cisplatin-resistance by suppressing DNA repair and promoting apoptosis pathways in ovarian carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Mar 15;13(3):239. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04568-4. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35293383 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs and ovarian cancer: a miRiad of mechanisms to induce cisplatin drug resistance.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2016;16(1):57-70. doi: 10.1586/14737140.2016.1121107. Epub 2015 Dec 5. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 26567444 Review.
References
-
- Kalamegam G, Sait KHW, Ahmed F, Kadam R, Pushparaj PN, Anfinan N, Rasool M, Jamal MS, Abu-Elmagd M, Al-Qahtani M. Human Wharton’s Jelly Stem Cell (hWJSC) extracts inhibit ovarian cancer cell lines OVCAR3 and SKOV3 in vitro by inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis [J]. Front Oncol. 2018;8:592. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

