The artificial intelligence revolution in gastric cancer management: clinical applications
- PMID: 40119433
- PMCID: PMC11929235
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-025-03756-4
The artificial intelligence revolution in gastric cancer management: clinical applications
Abstract
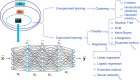
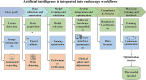
Nowadays, gastric cancer has become a significant issue in the global cancer burden, and its impact cannot be ignored. The rapid development of artificial intelligence technology is attempting to address this situation, aiming to change the clinical management landscape of gastric cancer fundamentally. In this transformative change, machine learning and deep learning, as two core technologies, play a pivotal role, bringing unprecedented innovations and breakthroughs in the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis evaluation of gastric cancer. This article comprehensively reviews the latest research status and application of artificial intelligence algorithms in gastric cancer, covering multiple dimensions such as image recognition, pathological analysis, personalized treatment, and prognosis risk assessment. These applications not only significantly improve the sensitivity of gastric cancer risk monitoring, the accuracy of diagnosis, and the precision of survival prognosis but also provide robust data support and a scientific basis for clinical decision-making. The integration of artificial intelligence, from optimizing the diagnosis process and enhancing diagnostic efficiency to promoting the practice of precision medicine, demonstrates its promising prospects for reshaping the treatment model of gastric cancer. Although most of the current AI-based models have not been widely used in clinical practice, with the continuous deepening and expansion of precision medicine, we have reason to believe that a new era of AI-driven gastric cancer care is approaching.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Diagnosis; Forecast; Gastric cancer; Research progress; Treat.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Application of artificial intelligence for improving early detection and prediction of therapeutic outcomes for gastric cancer in the era of precision oncology.Semin Cancer Biol. 2023 Aug;93:83-96. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2023.04.009. Epub 2023 Apr 26. Semin Cancer Biol. 2023. PMID: 37116818 Review.
-
Artificial intelligence for breast cancer detection and its health technology assessment: A scoping review.Comput Biol Med. 2025 Jan;184:109391. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.109391. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Comput Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 39579663
-
Artificial intelligence (AI) in restorative dentistry: current trends and future prospects.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Apr 18;25(1):592. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05989-1. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40251567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing the frontier of artificial intelligence on emerging technologies to redefine cancer diagnosis and care.Comput Biol Med. 2025 Jun;191:110178. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2025.110178. Epub 2025 Apr 13. Comput Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 40228444 Review.
-
Tribulations and future opportunities for artificial intelligence in precision medicine.J Transl Med. 2024 Apr 30;22(1):411. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05067-0. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38702711 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A retrospective analysis of Gastric Cancer Lymph Nodes Based on Groups, Regions, and Stages.Surg Pract Sci. 2025 May 29;21:100287. doi: 10.1016/j.sipas.2025.100287. eCollection 2025 Jun. Surg Pract Sci. 2025. PMID: 40530073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
-
- Alsina M, Arrazubi V, Diez M, et al. Current developments in gastric cancer: from molecular profiling to treatment strategy. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;20(3):155–70. - PubMed
-
- López MJ, Carbajal J, Alfaro AL, et al. Characteristics of gastric cancer around the world. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2023;181:103841. - PubMed
-
- Thrift AP, Wenker TN, El-Serag HB. Global burden of gastric cancer: epidemiological trends, risk factors, screening and prevention. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2023;20(5):338–49. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- XCXZZSS2024026/Hebei Provincial Graduate Innovation Funding Project
- 82205314/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- C20231017/Hebei Province "333 Talent Project" Funding Project
- GZY-KJS-2023-013/Science and Technology Project of the State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- 23377701D/Key R&D Program of Hebei Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources