Inhalable Hsa-miR-30a-3p Liposomes Attenuate Pulmonary Fibrosis
- PMID: 40119620
- PMCID: PMC12097057
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202405434
Inhalable Hsa-miR-30a-3p Liposomes Attenuate Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
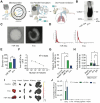
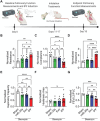
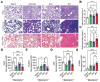
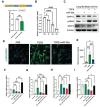
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) remains an incurable form of interstitial lung disease with sub-optimal treatments that merely address adverse symptoms or slow fibrotic progression. Here, inhalable hsa-miR-30a-3p-loaded liposomes (miR-30a) for the treatment of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice are presented. It was previously found that exosomes (Exo) derived from lung spheroid cells are therapeutic in multiple animal models of pulmonary fibrosis and are highly enriched for hsa-miR-30a-3p. The present study investigates this miRNA as a singular factor to treat IPF. Liposomes containing miR-30a mimic can be delivered to rodents through dry powder inhalation. Inhaled miR-30a and Exo consistently lead to improved pulmonary function across six consecutive pulmonary function tests and promote de-differentiation of profibrotic myofibroblasts. The heterogenous composure of Exo also promotes reparative alveolar type I and II cell remodeling and vascular wound healing through broad transforming growth factor-beta signaling downregulation, while miR-30a targets myofibroblast de-differentiation through CNPY2/PERK/DDIT3 signaling. Overall, inhaled miR-30a represses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of myofibroblasts, providing fibrotic attenuation and subsequent improvements in pulmonary function.
Keywords: CNPY2; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; inhalation; miR‐30a‐3p.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Richeldi L., Collard H. R., Jones M. G., Lancet 2017, 389, 1941. - PubMed
-
- Raghu G., Collard H. R., Egan J. J., Martinez F. J., Behr J., Brown K. K., Colby T. V., Cordier J., Flaherty K. R., Lasky J. A., Lynch D. A., Ryu J. H., Swigris J. J., Wells A. U., Ancochea J., Bouros D., Carvalho C., Costabel U., Ebina M., Hansell D. M., Johkoh T., Kim D. S., King Jr T. E., Kondoh Y., Myers J., Müller N. L., Nicholson A. G., Richeldi L., Selman M., Dudden R. F., et al., Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Richeldi L., du Bois R. M., Raghu G., Azuma A., Brown K. K., Costabel U., Cottin V., N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2071. - PubMed
-
- Noble P. W., Albera C., Bradford W. Z., Costabel U., Glassberg M. K., Kardatzke D., King Jr T. E., Lancaster L., Sahn S. A., Szwarcberg J., Valeyre D., du Bois R. M., Lancet 2011, 377, 1760. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL146153/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL146153/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- KL2TR001874/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HL144002/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL144002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 19EIA34660286/American Heart Association
- HL123920/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR001874/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HL149940/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HL154154/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- T35 OD011070/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL164998/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL149940/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL170612/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL171822/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL123920/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL170612/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL154154/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL164998/NH/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
