Galectin-3 regulates erythropoiesis and enhances the immunoregulatory properties of CD71+ erythroid cells across developmental stages
- PMID: 40119673
- PMCID: PMC12207073
- DOI: 10.1093/jimmun/vkaf020
Galectin-3 regulates erythropoiesis and enhances the immunoregulatory properties of CD71+ erythroid cells across developmental stages
Abstract
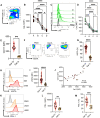
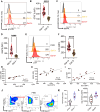
Galectins are expressed by different immune and nonimmune cells with diverse immunomodulatory properties. However, their roles in erythropoiesis remain unknown. We investigated the expression of galectin genes in splenic CD71+ erythroid cells (CECs) from neonatal BALB/c mice at various developmental stages using bulk RNA sequencing. Our analysis revealed distinct gene expression profiles at different ages. Specifically, CECs from day-3 mice had a markedly different expression pattern compared to those from days 6, 12, and 28. Notably, Lgals1, Lgals3, Lgals4, Lgals8, and Lgals9 were constitutively expressed in CECs, with galectin-3 (Gal-3) showing predominant surface expression, unlike Gal-1 and Gal-9. Further analysis revealed that Gal-3+ CECs exhibited elevated levels of TGF-β, ROS, arginase I, VISTA, and PD-L1, correlating with enhanced immunosuppressive functions. These cells also demonstrated increased CD45, c-kit, Ki67, and p21 levels, indicating heightened proliferative activity despite showing increased apoptosis. Moreover, we found that Gal-3+ CECs displayed enhanced activation of signaling pathways, including STAT5, MAPK, and LCK. Additionally, Gal-3+ CECs co-expressed Fas and FasL, implicating these molecules in the regulation of early erythroblasts. Notably, Gal-3 interacted with CD71 and GARP, influencing CECs' immunoregulatory roles. In tissue-specific studies, we found varying frequencies of Gal-3+ CECs across the spleen, liver, and bone marrow (BM), with notable variations in the placenta and fetal liver. These results were paralleled in human BM-derived CECs, which also exhibited high Gal-3 levels. Our findings emphasize the critical role of Gal-3 in modulating erythropoiesis and suggest that Gal-3+ CECs possess enhanced immunoregulatory capacities.
Keywords: GARP; erythroid progenitors; galectin-1; galectin-9; transferrin receptor.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The American Association of Immunologists.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Immunomodulatory effect of CD71+ erythroid cells in patients with kidney failure.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Aug 6;26(1):439. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04376-w. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40770293 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Matters: Physiological Abundance of Immuno-Regulatory CD71+ Erythroid Cells Impair Immunity in Females.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 21;12:705197. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.705197. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34367164 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-3 secreted by triple-negative breast cancer cells regulates T cell function.Neoplasia. 2025 Feb;60:101117. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2024.101117. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Neoplasia. 2025. PMID: 39729650 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal and neonatal outcomes of elective induction of labor.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2009 Mar;(176):1-257. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2009. PMID: 19408970 Free PMC article.
-
Nivolumab for adults with Hodgkin's lymphoma (a rapid review using the software RobotReviewer).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 12;7(7):CD012556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30001476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elahi S. Neglected cells: immunomodulatory roles of CD71(+) erythroid cells. Trends Immunol. 2019;40:181–185. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

