Unveiling the future of cancer stem cell therapy: a narrative exploration of emerging innovations
- PMID: 40120008
- PMCID: PMC11929669
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-02102-4
Unveiling the future of cancer stem cell therapy: a narrative exploration of emerging innovations
Abstract
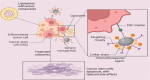
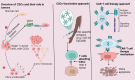
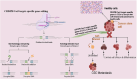
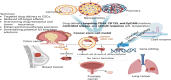
Cancer stem cells (CSCs), are a critical subpopulation within tumours, and are defined by their capacity for self-renewal, differentiation, and tumour initiation. These unique traits contribute to tumour progression, metastasis, and resistance to conventional treatments like chemotherapy and radiotherapy, often resulting in cancer recurrence and poor patient outcomes. As such, CSCs have become focal points in developing advanced cancer therapies. This review highlights progress in CSC-targeted treatments, including chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy, immunotherapy, molecular targeting, and nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems. Plant-derived compounds and gene-editing technologies, such as clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR), are explored for their potential to enhance precision and minimize side effects. Metabolic pathways integral to CSC survival, such as mitochondrial dynamics, mitophagy (regulated by dynamin-related protein 1 [DRP1] and the PINK1/Parkin pathway), one-carbon metabolism, amino acid metabolism (involving enzymes like glutaminase (GLS) and glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH]), lipid metabolism, and hypoxia-induced metabolic reprogramming mediated by hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF-1α and HIF-2α), are examined as therapeutic targets. The adaptability of CSCs through autophagy, metabolic flexibility, and epigenetic regulation by metabolites like α-ketoglutarate, succinate, and fumarate is discussed. Additionally, extracellular vesicles and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD⁺) metabolism are identified as pivotal in redox balance, DNA repair, and epigenetic modifications. Addressing challenges such as tumour heterogeneity, immune evasion, and treatment durability requires interdisciplinary collaboration. Advancing CSC-targeted therapies is essential for overcoming drug resistance and preventing cancer relapse, paving the way for transformative cancer treatments. This review underscores the importance of leveraging innovative technologies and fostering collaboration to revolutionize cancer treatment.
Keywords: CAR T-cell therapy; Cancer stem cells (CSCs); Chemotherapeutic drug resistance; Gene editing methods; Nanoparticular drug delivery; Tumour initiation and progression.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All Authors read and approved the manuscript for publication. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Statement of animal rights: Not applicable. Statement of informed consent: Not applicable.
Figures

References
-
- Bhat GR, Sethi I, Sadida HQ, Rah B, Mir R, Algehainy N, Albalawi IA, Masoodi T, Subbaraj GK, Jamal F, Singh M, Kumar R, Macha MA, Uddin S, Akil ASA-S, Haris M, Bhat AA. Cancer cell plasticity: from cellular, molecular, and genetic mechanisms to tumor heterogeneity and drug resistance. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024;43:197–228. 10.1007/s10555-024-10172-z. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Johari B, Ebrahimi-Rad M, Maghsood F, Lotfinia M, Saltanatpouri Z, Teimoori-Toolabi L, Sharifzadeh Z, Karimipoor M, Kadivar M. Myc Decoy oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits growth and modulates differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells as a model of cancer stem cells. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017;17:1786–95. 10.2174/1871521409666170412142507. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
