Detection of minimal residual disease and prediction of recurrence in breast cancer using a plasma-only circulating tumor DNA assay
- PMID: 40120523
- PMCID: PMC11982450
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2025.104296
Detection of minimal residual disease and prediction of recurrence in breast cancer using a plasma-only circulating tumor DNA assay
Abstract
Background: Detection of minimal residual disease (MRD) in early breast cancer (EBC) after curative-intent treatment may identify patients at risk for recurrence. Most circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA)-based MRD assays require knowledge of genomic alterations from tumor tissue. However, tissue availability may be limited in some patients. Here, we evaluated sensitivity and specificity for recurrence detection, using a plasma-only ctDNA MRD assay.
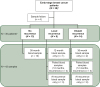
Materials and methods: For this pilot study, 47 plasma samples from 38 EBC patients were collected at 12 or 36 months post-diagnosis or at clinical recurrence. ctDNA presence was determined by a custom bioinformatics classifier that identifies tumor-derived somatic variants and methylation profiles specific to individual cancer types using a 5-Mb next-generation sequencing panel.
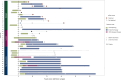
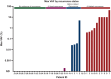
Results: ctDNA was detected at or before distant recurrence in 11/14 (79%) patients [sensitivity was 85% (11/13) among samples collected within 2 years from recurrence]. Lead time was evaluable in 4/6 (67%) samples collected before distant recurrence with detectable ctDNA and ranged from 3.4 to 18.5 months. ctDNA was not detected in samples from patients without recurrence (n = 13).
Conclusions: This study demonstrates the feasibility of MRD detection in EBC using a plasma-only multiomic ctDNA-based approach. Larger studies are ongoing to further validate the clinical performance of the assay and demonstrate its applications.
Keywords: MRD; breast cancer recurrence; circulating tumor DNA; ctDNA; early breast cancer; minimal residual disease.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J., Colombet M., Soerjomataram I., et al. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int J Cancer. 2019;144:1941–1953. - PubMed
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG) Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet Lond Engl. 2005;365:1687–1717. - PubMed
-
- Cardoso F., Kyriakides S., Ohno S., et al. Early breast cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2019;30:1194–1220. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

