Predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer via interpretable multimodal deep learning
- PMID: 40121304
- PMCID: PMC11929913
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-025-01560-y
Predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer via interpretable multimodal deep learning
Abstract
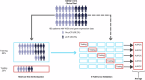
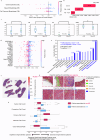
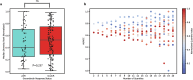
Building accurate prediction models and identifying predictive biomarkers for treatment response in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer (MIBC) are essential for improving patient survival but remain challenging due to tumor heterogeneity, despite numerous related studies. To address this unmet need, we developed an interpretable Graph-based Multimodal Late Fusion (GMLF) deep learning framework. Integrating histopathology and cell type data from standard H&E images with gene expression profiles derived from RNA sequencing from the SWOG S1314-COXEN clinical trial (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02177695 2014-06-25), GMLF uncovered new histopathological, cellular, and molecular determinants of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Specifically, we identified key gene signatures that drive the predictive power of our model, including alterations in TP63, CCL5, and DCN. Our discovery can optimize treatment strategies for patients with MIBC, e.g., improving clinical outcomes, avoiding unnecessary treatment, and ultimately, bladder preservation. Additionally, our approach could be used to uncover predictors for other cancers.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Bishoy M Faltas: Consulting or Advisory Role: QED therapeutics, Boston Gene, Astrin Biosciences Merck, Immunomedics/Gilead, QED therapeutics, Guardant, Janssen. Patent Royalties: Immunomedics/Gilead. Research support: Eli Lilly. Honoraria: Urotoday. Grants and research support: NIH, DoD-CDMRP, Starr Cancer Consortium, P-1000 Consortium. Olivier Elemento: Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Freenome, OneThree Biotech, Owkin, Volastra Therapeutics. Personal fees: Pionyr Immunotherapeutics, Champions Oncology. Seth P Lerner: Research support for Clinical trials - Aura Bioscience, FKD, JBL (SWOG), Genentech (SWOG), Merck (Alliance), QED Therapeutics, Surge Therapeutics, Vaxiion; Consultant/Advisory Board - Aura Bioscience, BMS, C2iGenomics, Immunity Bio, Incyte, Gilead, Pfizer/EMD Serono, Protara, Surge Therapeutics, UroGen, Vaxiion, Verity; Patent – TCGA classifier; Honoraria – Grand Rounds Urology, UroToday. Zilong Bai, Mohamed Osman, Matthew Brendel, Catherine M. Tangen, Thomas W. Flaig, Ian M. Thompson, Melissa Plets, M. Scott Lucia, Dan Theodorescu, Daniel Gustafson, Siamak Daneshmand, Joshua J. Meeks, Woonyoung Choi, Colin P. N. Dinney, David J. McConkey, and Fei Wang declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: The study was reviewed and received approval by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) Central Institutional Review Board (CIRB), and patients provided written, informed consent; it was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki guidelines17.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., Fuchs, H. E. & Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin.72, 7–33 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Novara, G. et al. Complications and mortality after radical cystectomy for bladder transitional cell cancer. J. Urol. 10.1016/j.juro.2009.05.032 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Shabsigh, A. et al. Defining early morbidity of radical cystectomy for patients with bladder cancer using a standardized reporting methodology. Eur. Urol.55, 164–174 (2009). - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U10CA180888/NIH/NCI grants
- U10CA180888/NIH/NCI grants
- U10CA180888/NIH/NCI grants
- U10CA180888/NIH/NCI grants
- U10CA180888/NIH/NCI grants
- U10CA180888/NIH/NCI grants
- U10CA180888/NIH/NCI grants
- U10CA180888/NIH/NCI grants
- U10CA180888/NIH/NCI grants
- U10CA180888/NIH/NCI grants
- U10CA180888/NIH/NCI grants
- U10CA180888/NIH/NCI grants
- U10CA180888/NIH/NCI grants
- U10CA180888/NIH/NCI grants
- U10CA180888/NIH/NCI grants
- U10CA180888/NIH/NCI grants
- U10CA180888/NIH/NCI grants
- U10CA180888/NIH/NCI grants
- U10CA180888/NIH/NCI grants
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

