Improving executive functioning and reducing the risk of Alzheimer's disease with music therapy: A narrative review of potential neural mechanisms
- PMID: 40123371
- PMCID: PMC12231918
- DOI: 10.1177/13872877251327762
Improving executive functioning and reducing the risk of Alzheimer's disease with music therapy: A narrative review of potential neural mechanisms
Abstract
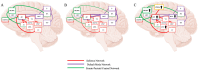
The incidence of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and the concurrent cost of healthcare will increase as the population continues to age. Pharmaceutical interventions effectively manage symptoms of AD but carry side effects and ineffectively address underlying causes and disease prevention. Non-pharmaceutical interventions for AD, such as music training and therapy do not carry these side effects and can improve symptoms, and should therefore be explored as stand-alone or co-therapy for AD. In addition, music encapsulates modifiable lifestyle factors, such as cognitive stimulation, that have been shown to delay progression of and prevent AD. However, the neural mechanisms underpinning how music improves AD symptoms are not fully understood and whether music can target compensatory processes, activate neural networks, or even slow or prevent AD needs further research. Research suggests neural mechanism may involve stimulating brain areas to promote neurogenesis, dopaminergic rewards systems, and the default mode network (DMN). Alternatively, this review proposes that music improve symptoms of AD via the fronto-parietal control network (FPCN), the salience network (SN) and DMN, and neural compensation. This review will then present evidence for how music could activate the FPCN, SN, and DMN to improve their efficiency, organization, and cognitive functions they govern, protecting the brain from damage, slowing progression, and possibly preventing AD. Establishing how music improves symptoms of AD can lead to tailored music therapy protocols that target functional neural networks responsible for impaired executive functions common in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; executive functioning; health intervention; music training and therapy; neural networks.
Figures
References
-
- Livingston G, Huntley J, Liu KY, et al. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care: 2024 report of the Lancet standing commission. Lancet 2024; 404: 572–628. - PubMed
-
- Power R, Prado-Cabrero A, Mulcahy R, et al. The role of nutrition for the aging population: implications for cognition and Alzheimer's disease. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 2019; 10: 619–639. - PubMed
-
- Niu H, Álvarez-Álvarez I, Guillén-Grima F, et al. Prevalence and incidence of Alzheimer's disease in Europe: a meta-analysis. Neurología 2017; 32: 523–532. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

