Hippocampal Inhibitory Interneuron-Specific DREADDs Treatment Alters mTORC1-4E-BP Signaling and Impairs Memory Formation
- PMID: 40123570
- PMCID: PMC11931476
- DOI: 10.1111/jnc.70048
Hippocampal Inhibitory Interneuron-Specific DREADDs Treatment Alters mTORC1-4E-BP Signaling and Impairs Memory Formation
Abstract
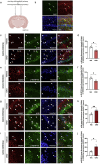
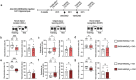
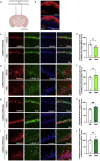
Control of protein synthesis via the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) is essential for learning and memory. However, the cell-type-specific and spatiotemporal regulation of this pathway during memory formation is not well understood. In this study, we expressed artificial human muscarinic M3 [hM3D(Gq)] or M4 [hM4D(Gi)] designer receptors exclusively activated by designer drugs (DREADDs) in hippocampal CA1 excitatory or inhibitory neurons of adult mice. We studied the impact of clozapine-N-oxide (CNO), a synthetic DREADDs agonist, on the mTORC1 pathway and long-term memory. hM3D(Gq) and hM4D(Gi) activate or inactivate, respectively, mTORC1 signaling in hippocampal interneurons, as indicated by the phosphorylation of its targets, eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding proteins (4E-BP1/2) and ribosomal protein S6 (S6). Activation of either hM3D(Gq) or hM4D(Gi) in mice immediately after training in memory tasks impaired long-term memory formation in inhibitory, but not in excitatory neurons. The findings underscore the importance of activity-dependent mTORC1-4E-BP1/2 signaling in hippocampal inhibitory interneurons for memory formation.
Keywords: 4E‐BP; clozapine‐N‐oxide; hippocampus; interneurons; mTORC1; memory.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Neurochemistry published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of International Society for Neurochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Alapin, J. M. , Mohamed M. S., Shrestha P., et al. 2023. “Opto4E‐BP, an Optogenetic Tool for Inducible, Reversible, and Cell Type‐Specific Inhibition of Translation Initiation.” bioRxiv 10.1101/2023.08.30.554643. - DOI
-
- Alcacer, C. , Andreoli L., Sebastianutto I., Jakobsson J., Fieblinger T., and Cenci M. A.. 2017. “Chemogenetic Stimulation of Striatal Projection Neurons Modulates Responses to Parkinson's Disease Therapy.” Journal of Clinical Investigation 127, no. 2: 720–734. 10.1172/jci90132. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

