Decreasing interleukin-6 levels after TIPS predict outcomes in decompensated cirrhosis
- PMID: 40124165
- PMCID: PMC11929062
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2024.101308
Decreasing interleukin-6 levels after TIPS predict outcomes in decompensated cirrhosis
Abstract
Background & aims: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) effectively treats complications of cirrhosis. Systemic inflammation (SI) is linked to acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) and liver-related death. We aimed to assess the trajectory and clinical impact of SI parameters after TIPS implantation.
Methods: Consecutive patients undergoing elective implantation of covered TIPS for recurrent/refractory ascites or portal-hypertensive bleeding at the Medical University Vienna (NCT03409263; n = 58) and at the Hannover Medical School (NCT04801290, n = 51) were included. IL-6 was assessed at baseline (BL), 3 months (M3) and up to 6 (M6; Hannover cohort) or 9 months (M9; Vienna cohort) of follow-up; C-reactive protein (CRP) and lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP) were assessed in the Vienna cohort only.
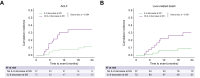
Results: In 109 patients (66.1% male, median age 57 years) receiving TIPS mainly (72.4%) by indication ascites the median BL IL-6 levels were 10.5 pg/ml; and 41.3% (n = 45/109) patients exhibiting IL-6 ≥14 pg/ml. From BL to M3, IL-6 decreased in 63.8% (n = 37/58; Vienna cohort) and in 68.6% (n = 35/51; Hannover cohort) of patients, respectively. Similar rates of decreases were observed also for CRP (in 62.1%) and for LBP (in 77.4%). A considerable IL-6 reduction (≥50% of baseline) was noted in 41 (37.6%) patients during follow-up. Competing risk regression in the combined cohort adjusted for age, albumin, and model for end-stage liver disease revealed that IL-6 decrease at M3 was an independently protective factor for the development of ACLF (adjusted subdistribution hazard ratio [asHR]: 0.26; 95% CI: 0.09-0.77; p = 0.016) and liver-related death (asHR: 0.26; 95% CI: 0.07-0.95; p = 0.042).
Conclusions: TIPS leads to a sustained reduction of SI and bacterial translocation in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. Decreasing IL-6 levels three months after TIPS implantation indicate a lower risk of ACLF and liver-related death in patients with cirrhosis.
Impact and implications: Systemic inflammation is a major driver of disease progression in patients with decompensated advanced chronic liver disease (dACLD). This study demonstrates that systemic inflammation (i.e. interleukin-6 [IL-6]) effectively and sustainedly decreases after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) implantation. A decrease of IL-6 3 months after TIPS implantation is a protective factor for acute-on-chronic liver failure and liver-related death. Thus, our results suggest that TIPS reduces systemic inflammation in a clinically meaningful way.
Keywords: Acute-on-chronic liver failure; Bacterial translocation; Systemic inflammation; Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose regarding the work under consideration for publication. Conflicts of interests outside the submitted work: AK, AT, PH, JK, TM, LS, HR, LR, ND, GK, CF, BM, and LH declare no conflicts of interest. MT received research grants, travel grants, speaker fees, and advised for Gilead Sciences; received consultancy fees from AbbVie, Albireo, Agomab, BiomX, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chemomab, Falk, GlaxoSmithKline, Genfit, Hightide, Intercept, Ipsen, Jannsen, Mirum, MSD, Novartis, Pliant, Regulus, Siemens and Shire; research funding from Albireo, Alnylam, Cymabay, Falk, Intercept, MSD, Takeda, and UltraGenyx; travel grants from AbbVie, Falk, Intercept and Jannsen; speaker fees from Albireo, BMS, Falk, Intercept, Ipsen, MSD, and Madrigal; the Medical Universities of Graz and Vienna have filed patents on medical use of norUDCA and MT is listed as co-inventor. MM served as a speaker and/or consultant and/or advisory board member for AbbVie, Collective Acumen, Gilead, Takeda, and W.L. Gore & Associates and received travel support from AbbVie and Gilead. TR served as a speaker and/or consultant and/or advisory board member for AbbVie, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, Intercept, MSD, Siemens, and W.L. Gore & Associates and received grants/research support from AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, Intercept, MSD, Myr Pharmaceuticals, Pliant, Philips, Siemens, and W.L. Gore & Associates as well as travel support from AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, and Roche. BM reports lecture and/or consultant fees from AbbVie, Astella, BMS, Falk, Fujirebio, Gilead, Luvos, MSD, Norgine, Roche, and W.L. Gore & Associates. He received research support from Altona, EWIMED, Fujirebio, and Roche. Please refer to the accompanying ICMJE disclosure forms for further details.
Figures


References
-
- D'Amico G., Garcia-Tsao G., Pagliaro L. Natural history and prognostic indicators of survival in cirrhosis: a systematic review of 118 studies. J Hepatol. 2006;44:217–231. - PubMed
-
- Costa D., Simbrunner B., Jachs M., et al. Systemic inflammation increases across distinct stages of advanced chronic liver disease and correlates with decompensation and mortality. J Hepatol. 2021;74:819–828. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

