Identification and analysis of oxidative stress-related genes in endometriosis
- PMID: 40124382
- PMCID: PMC11925871
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1515490
Identification and analysis of oxidative stress-related genes in endometriosis
Abstract
Background: Early diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis (EM) remain challenging because of the lack of knowledge about EM development. While oxidative stress (OS) has been associated with EM, the link is unclear. We explored OS-related genes (OSRGs) and their role in EM pathogenesis.
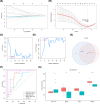
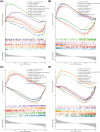
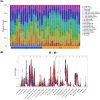
Material and methods: We combined two ectopic endometrium (EC) and eutopic endometrium (EU) datasets (GSE11691 and GSE25628) into a dataset for analysis. Bioinformatic analyses were used to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs), OS-related genes (OSRGs), enriched pathways, competitive endogenous RNA network, and immune cell infiltration. Finally, real time-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and Western blot (WB) were used to validate the expression of key OSRGs in clinical patient samples.
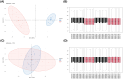
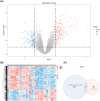
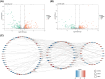
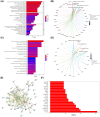
Results: Bioinformatic analysis identified 459 DEGs between EC and EU samples, including 67 OSRGs. A ceRNA network was established, encompassing 28 DE-OSRGs, 32 miRNAs, and 53 lncRNAs. Four key OSRGs (CYP17A1, NR3C1, ENO2, and NGF) were selected from protein-protein interaction network analysis. The RT-qPCR and WB analysis showed that these genes' abnormal changes in RNA and protein levels were consistent with data in public databases. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis identified three immune-related OSRGs (CYP17A1, NR3C1, and NGF) and 20 lncRNAs that may regulate NR3C1 through 10 miRNAs.
Conclusion: The key OSRGs may function via multilayered networks in EM. We provide insights into EM and underscore the potential significance of OSRGs and the immune environment for diagnostic and prognosis evaluation.
Keywords: ectopic endometrium; endometriosis; eutopic endometrium; immune cells; lncRNA; machine learning; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2025 Xie, Lu, Lv, Kong and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
LINC01018 and SMIM25 sponged miR-182-5p in endometriosis revealed by the ceRNA network construction.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2020 Jan-Dec;34:2058738420976309. doi: 10.1177/2058738420976309. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33237828 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Key Genes and Pathways associated with Endometriosis by Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Aug 3;18(15):3425-3436. doi: 10.7150/ijms.63541. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34522169 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of characteristic genes and ceRNA regulation mechanism of endometriosis based on full transcriptional sequencing.Front Genet. 2022 Jul 22;13:902329. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.902329. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35938015 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics identification and validation of biomarkers and infiltrating immune cells in endometriosis.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 29;13:944683. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.944683. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36524127 Free PMC article.
-
Endometriosis: A new perspective on epigenetics and oxidative stress.J Reprod Immunol. 2025 Jun;169:104462. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2025.104462. Epub 2025 Feb 21. J Reprod Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40010026 Review.
Cited by
-
miRNA in Endometriosis-A New Hope or an Illusion?J Clin Med. 2025 Jul 8;14(14):4849. doi: 10.3390/jcm14144849. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40725541 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vitagliano A, Noventa M, Quaranta M, Gizzo S. Statins as targeted “Magical pills” for the conservative treatment of endometriosis: may potential adverse effects on female fertility represent the “Dark side of the same coin”? A systematic review of literature. Reprod Sci. (2016) 23:415–28. doi: 10.1177/1933719115584446 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

