Intratumoral administration of Hibiscus sabdariffa- derived anthocyanins exerts potent antitumor effects in murine cancer models
- PMID: 40124386
- PMCID: PMC11925877
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1549890
Intratumoral administration of Hibiscus sabdariffa- derived anthocyanins exerts potent antitumor effects in murine cancer models
Abstract
Introduction: Cancer remains the leading cause of death worldwide, with increasing incidence rates. Natural compounds have gained attention as potential therapeutic agents due to their bioactive properties. Anthocyanins, particularly delphinidin-3-sambubioside (Dp-3-sam) and cyanidin-3-sambubioside (Cn-3-sam), are flavonoids with antioxidant and potential antitumor properties. This study investigates the antitumor effects of anthocyanins extracted from Hibiscus sabdariffa L. (H. sabdariffa), administered intratumorally, and their potential as adjuvants to chemotherapy.
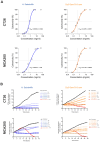
Methods: Anthocyanins were extracted from H. sabdariffa and characterized using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The total phenolic content was determined using the Folin-Ciocalteu method. Antioxidant activity was assessed through DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP assays. The antiproliferative effects of Dp-3-sam and Cn-3-sam were evaluated in vitro using MCA-205 fibrosarcoma and CT26 colon carcinoma cell lines. In vivo studies were conducted on mouse tumor models to assess tumor growth inhibition following intratumoral administration of anthocyanins alone or in combination with doxorubicin. The impact on angiogenesis, immune cell recruitment, and long-term immune memory was also analyzed.
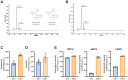
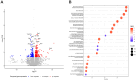
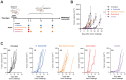
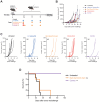
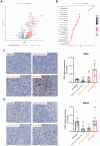
Results: HPLC analysis confirmed the presence of Dp-3-sam and Cn-3-sam in the H. sabdariffa extract. The anthocyanins exhibited significant antioxidant activity in all assays. In vitro studies demonstrated dose-dependent inhibition of cancer cell proliferation. In vivo, intratumoral administration of anthocyanins led to a significant reduction in tumor growth. The combination of anthocyanins with doxorubicin further enhanced tumor suppression. Mechanistically, Dp-3-sam and Cn-3-sam reduced angiogenesis and promoted immune cell recruitment but did not elicit an effective antitumor immune response alone. However, co-administration with doxorubicin reversed this limitation, leading to increased immune activation and resistance to tumor rechallenge, suggesting the induction of long-term immune memory.
Discussion: These findings highlight the potential of H. sabdariffa-derived anthocyanins as adjuvants in cancer therapy. When administered intratumorally, they enhance chemotherapy efficacy and immunogenicity. However, further studies are needed to optimize dosing strategies, evaluate long-term safety, and assess clinical applicability.
Keywords: Hibiscus sabdariffa L.; anthocyanins; antitumor activity; immune modulation; intratumoral therapy.
Copyright © 2025 Ezcurra-Hualde, Gómez-Leyva, Juarez-Curiel, Regalado-Noyola, Ardaiz, Casares, Ruiz-Guillamon, Rodríguez-Leon, Flores-Hernández, Arrizabalaga, Risson, García-Fuentes, Gomar, Belsue, Aranda, Berraondo and Garcia-Garcia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

