Dyskalemia Prior to and After Initiation of a Fixed Dose Combination of Telmisartan and Amlodipine in Adults with Hypertension in Bangladesh
- PMID: 40124766
- PMCID: PMC11927674
- DOI: 10.5334/gh.1415
Dyskalemia Prior to and After Initiation of a Fixed Dose Combination of Telmisartan and Amlodipine in Adults with Hypertension in Bangladesh
Abstract
Background: The World Health Organization recommends fixed-dose combination (FDC) pills for treating hypertension. Antihypertensive FDC pills often contain a renin-angiotensin inhibitor (RASI) or diuretic. Thus, screening and monitoring for dyskalemia (hypokalemia or hyperkalemia) before and after starting these classes of medications are recommended, a significant barrier for implementation in resource-limited settings. However, the need for blood tests may be overemphasized if the prevalence of dyskalemia in patients with hypertension is uncommon and the incidence of dyskalemia is rare after initiation of FDC.
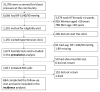
Methods: We conducted a community-based blood pressure (BP) screening program in Dhaka, Bangladesh, and determined the prevalence of dyskalemia, as defined by K < 3.0 or K > 5.5 mmol/L, in untreated adults with SBP ≥140 mmHg and/or DBP ≥90 mmHg. Among those with a baseline serum K of ≥3.0 or ≤5.0 mmol/L and creatinine clearance ≥30 ml/min, we determined the incidence of dyskalemia 2 months after initiation of a daily FDC of telmisartan 40 mg and amlodipine 5 mg. Secondary outcomes were BP change, medication adherence, and symptoms.
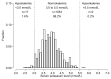
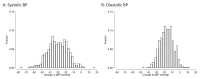
Results: In 2022-2023, we recruited 1,073 adults with SBP ≥140 mmHg and/or DBP ≥90 mmHg. The mean age was 54 years, with 71% men and mean baseline BP 157/94 (SD 12/9.3) mmHg. The prevalence of hypokalemia and hyperkalemia was 1.6% and 0.2%, respectively. FDC was initiated in 1,017 eligible patients, and 864 completed the 2-month follow-up visit. Incident hypokalemia occurred in 1.5% of patients, but there was no case of incident hyperkalemia. The mean change in serum potassium after initiating FDC was -0.05 (0.53) mmol/L. At follow-up, 92% had BP <140/90 mmHg with a mean SBP change of -29.8 mmHg. 1% self-reported mild symptoms (e.g., leg swelling), and there was one death of undetermined cause.
Conclusions: Given low prevalence and incidence of hyperkalemia and evident reduction in BP, our study suggests initiating FDC with telmisartan and amlodipine may be a practical and safe option for newly diagnosed hypertension, especially in resource-constrained settings where blood tests cannot be easily obtained.
Keywords: Fixed-dose combination; Hyperkalemia; Hypertension; Hypokalemia.
Copyright: © 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial relationships or conflicts of interest relevant to this article to disclose. This study was presented in an abstract form at the American Heart Association Hypertension Scientific Sessions (September 2023, Boston, MA).
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

