Telelactation Support in Emergency Situations: Experiences From the Recent Devastating Earthquakes in Turkey
- PMID: 40125143
- PMCID: PMC11929972
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.79399
Telelactation Support in Emergency Situations: Experiences From the Recent Devastating Earthquakes in Turkey
Abstract
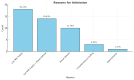
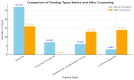
Breastfeeding initiation within the first hour of birth, exclusive breastfeeding for six months, and continuation up to two years or beyond, even during emergencies, are generally recommended. However, challenges in breastfeeding support in emergencies often result in increased infant vulnerability and reliance on formula feeding. This retrospective study evaluates telelactation services provided by the "Disaster Area Parent Support Group" after the devastating February 2023 earthquakes in Turkey. Telelactation, a telemedicine-based breastfeeding counseling method, was implemented to address breastfeeding challenges in disaster-affected regions. Between February and September 2023, 46 mothers received telelactation counseling. Most consultations addressed issues such as low milk supply, breast refusal, and relactation. Following an average of 9.11 consultations per mother over 16.69 weeks, exclusive breastfeeding rates increased significantly, with 32.56% of infants exclusively breastfed compared to 6.98% at admission. Additionally, successful relactation was achieved in 71.42% of cases among mothers attempting it. All mothers reported satisfaction with the support received. This study highlights the critical role of telelactation in emergencies, particularly in regions with disrupted healthcare infrastructure. While not a substitute for in-person consultations, telelactation proved effective in resolving breastfeeding issues, improving infant feeding practices, and offering psychological support to mothers. The findings underscore the necessity of equipping healthcare providers with telemedicine skills to sustain breastfeeding during crises. Limitations include the small sample size and technological barriers in disaster zones. Future research should explore broader applications of telelactation in emergencies to enhance maternal and child health outcomes.
Keywords: baby care; breast milk; lactation consultant; natural baby care; tele medicine.
Copyright © 2025, Basibuyuk et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Istanbul Medipol University Faculty of Medicine Ethics Committee on October 27, 2023 issued approval 10840098-772.02-6875. Istanbul Medipol University Faculty of Medicine Ethics Committee approved this paper on October 27, 2023, with approval number 10840098-772.02-6875. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- UNICEF. Nutrition in emergencies: saving lives today, strengthening systems for tomorrow. [ Jan; 2024 ]. 2018. https://www.unicef.org/media/97011/file/Nutrition-in-emergencies-Saving-... https://www.unicef.org/media/97011/file/Nutrition-in-emergencies-Saving-...
-
- World Health Organization. Breastfeeding in emergency situations. Advocacy brief. [ Jan; 2024 ]. 2017. https://www.globalbreastfeedingcollective.org/media/376/file/Breastfeedi... https://www.globalbreastfeedingcollective.org/media/376/file/Breastfeedi...
-
- Lawrence RA. Breastfeeding: A Guide for the Medical Profession. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022. Biochemistry of human milk; pp. 93–146.
-
- Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 antigens and antibodies in breast milk. Keskindemirci G, Karabayir N, İstanbullu A, et al. İst Tıp Fak Derg. 2021;84:287–292.
-
- Breastfeeding: crucially important, but increasingly challenged in a market-driven world. Pérez-Escamilla R, Tomori C, Hernández-Cordero S, et al. Lancet. 2023;401:472–485. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources