Analysis between Helicobacter pylori infection and hepatobiliary diseases
- PMID: 40125519
- PMCID: PMC11926543
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1477699
Analysis between Helicobacter pylori infection and hepatobiliary diseases
Abstract
Objective: Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) represents a significant chronic health concern, affecting approximately half of the global population. While H. pylori infection has been closely linked to numerous extradigestive diseases, the relationship between H. pylori and lesions in the gallbladder and biliary tract remains under debate.
Method: We retrospectively collected data from patients who underwent H. pylori tests at the Physical Examination Center of Taizhou Central Hospital (Taizhou University Hospital) between 2018 and 2022. Logistic regression analysis and restricted cubic spline analysis were employed to investigate the correlation between parameters and H. pylori. Additionally, we utilized population data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database as an external validation cohort.
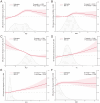
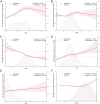
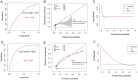
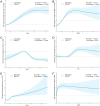
Results: A total of 30,612 patients were included in the training set, with 22,296 (72.8%) belonging to the H. pylori non-infection group and 8,316 (27.2%) to the H. pylori infection group. Compared to the non-infection group, patients in the infection group exhibited a significant decrease in albumin levels and a notable increase in total cholesterol and erythrocyte sedimentation rate levels. Furthermore, the infection group demonstrated significantly higher occurrences of gallbladder cholesterol crystals (6.0%), gallbladder polyps (20.2%), and atherosclerosis (25.6%) compared to the non-infection group, with respective rates of 5.1%, 19.1%, and 21.4% (average p < 0.05). However, no significant differences were observed between the two groups in terms of fatty liver, intrahepatic inflammation, gallstones, or cholecystitis. Additional regression analysis revealed that H. pylori, age, BMI, albumin, and total cholesterol were independent risk factors for the cholesterol crystals and atherosclerosis.
Conclusion: H. pylori infection is closely associated with the gallbladder cholesterol crystals and atherosclerosis, albeit not with conditions such as fatty liver, gallbladder stones, or cholecystitis. Future research necessitates multi-center, prospective studies to corroborate these findings.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; cholesterol crystal; fatty liver; gallbladder polyp; gallstone.
Copyright © 2025 Yu, Chen, Chen, Pan, Shao, Jin, Wang, Zhang, Lin, Feng and Teng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Helicobacter pylori and other Helicobacter species in gallbladder and liver of patients with chronic cholecystitis detected by immunological and molecular methods.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2005 Jan;40(1):96-102. doi: 10.1080/00365520410009546. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 15841721
-
Helicobacter pylori is not a contributing factor in gallbladder polyps or gallstones: a case-control matching study of Chinese individuals.J Int Med Res. 2020 Oct;48(10):300060520959220. doi: 10.1177/0300060520959220. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 33045881 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori infection is linked to metabolic dysfunction and associated steatotic liver disease: A large cross-sectional study.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 Apr 7;31(13):102563. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i13.102563. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40248064 Free PMC article.
-
The link between Helicobacter pylori infection and gallbladder and biliary tract diseases: A review.Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2023 Aug 31;27(3):241-250. doi: 10.14701/ahbps.22-056. Epub 2023 Jun 26. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2023. PMID: 37357161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Helicobacter pylori and hepatobiliary diseases].Clin Ter. 2003 Jan-Feb;154(1):55-6. Clin Ter. 2003. PMID: 12854285 Review. Italian.
References
-
- Abo-Amer Y. E.-E., Sabal A., Ahmed R., Hasan N. F. E., Refaie R., Mostafa S. M., et al. . (2020). Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in a developing country: a cross-sectional study. Diabetes Metab. Syndrome Obes. 13, 619–625. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S237866 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

