Expanding the therapeutic role of highly purified cannabidiol in monogenic epilepsies: A multicenter real-world study
- PMID: 40126049
- PMCID: PMC12291005
- DOI: 10.1111/epi.18378
Expanding the therapeutic role of highly purified cannabidiol in monogenic epilepsies: A multicenter real-world study
Abstract
Objective: This real-world, retrospective, multicenter study aims to investigate the effectiveness of highly purified cannabidiol (CBD) in a large cohort of patients with epilepsy of genetic etiology due to an identified monogenic cause. Additionally, we examine the potential relationship between specific genetic subgroups and treatment response.
Methods: This study was conducted across 27 epilepsy centers and included patients with monogenic epileptic disorders (pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants) who were treated with highly purified CBD for at least 3 months.
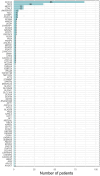
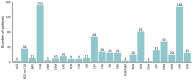
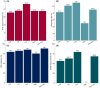
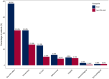
Results: A total of 266 patients (135 females, 50.8%) with monogenic epilepsies were included with a median age at CBD initiation of 12 years (interquartile range [IQR] = 7-19) and a median follow-up duration of 17 months (IQR = 12-24). Overall, 77 different monogenic epilepsies have been included, with the most common genes being SCN1A (32.3%), TSC2 (13.5%), CDKL5, and MECP2 (4.5% each). The mean seizure reduction at the last follow-up was 38.6%, with 47.5% of patients achieving ≥50% seizure reduction and 7.4% achieving seizure freedom. The Clinical Global Impression scale indicated improvement in 65.8% of patients. The general linear mixed model revealed that a shorter maximum duration of seizure freedom before CBD initiation and a higher degree of intellectual disability were independently associated with lower CBD effectiveness. Conversely, no significant differences in seizure outcome were observed across different epilepsy syndromes (Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, Dravet syndrome, tuberous sclerosis complex epilepsy, and other developmental and epileptic encephalopathy), between approved indications and off-label use, or between concomitant clobazam use or not.
Significance: This study supports CBD as a potential treatment for monogenic epilepsies beyond its licensed indications, demonstrating comparable effectiveness between approved and off-label use and suggesting genetic subgroups with promising treatment responses.
Keywords: CBD; Lennox–Gastaut syndrome; developmental and epileptic encephalopathy; effectiveness; epilepsy; intellectual disability.
© 2025 The Author(s). Epilepsia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International League Against Epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
E.C.I. reports speaking honoraria from Lusofarmaco, outside the submitted work. P.B.M. has served on an advisory board for Angelini Pharma and has received travel expenses from UCB Pharma, outside the submitted work. J.P.‐C. has served as a speaker and has received travel expenses from Angelini Pharma and LivaNova, outside the submitted work. V.D.G. has served on scientific advisory boards for Longboard Pharmaceuticals, has received research grants from Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and has received speaker and consultancy fees from Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Nutricia, Vitaflo, and Dr. Schar Kanso, outside the submitted work. J.D.‐C. has received speaker honoraria from Jazz Pharmaceuticals, outside the submitted work. F.B. has served on scientific advisory boards for Angelini Pharma, UCB, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Ethypharm, and Eisai and has received speaker honoraria from Angelini Pharma and UCB, outside the submitted work. Her research receives support from the Multidisciplinary Transition Model for Patients With Complex Epilepsy (Trans‐Epic) project, supported by Ricerca Corrente. S.M. has served on scientific advisory boards for Zogenix, UCB, and Ethypharm and has received speaker honoraria for Biocodex, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Eisai, and UCB, outside the submitted work. N.D. has served as a paid advisor and/or speaker for Actiobio Sciences, Angelini Pharma, Bial, Eisai, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, LivaNova, and UNEEG Medical, outside the submitted work. C.D.B. reports personal fees from UCB Pharma, Eisai, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Angelini Pharma, Lusofarmaco, and Ecupharma, outside the submitted work. G.R. has served on advisory boards or received speaker honoraria paid to her department from Angelini, Bial, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Neuraxpharm, Neurocrine, and Takeda, outside the submitted work. Her research receives support from the Swiss National Science (SNSF: 208184) and Anna Mueller Grocholski Foundations. The other authors report no disclosures relevant to this article. We confirm that we have read the Journal's position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
Figures
References
-
- Thiele EA, Marsh ED, French JA, Mazurkiewicz‐Beldzinska M, Benbadis SR, Joshi C, et al. Cannabidiol in patients with seizures associated with Lennox‐Gastaut syndrome (GWPCARE4): a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10125):1085–1096. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30136-3 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

