Unleashing the Power of Multiomics: Unraveling the Molecular Landscape of Peripheral Neuropathy
- PMID: 40126913
- PMCID: PMC12040521
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.70019
Unleashing the Power of Multiomics: Unraveling the Molecular Landscape of Peripheral Neuropathy
Abstract
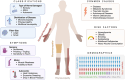
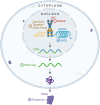
Peripheral neuropathies (PNs) affect over 20 million individuals in the United States, manifesting as a wide range of sensory, motor, and autonomic nerve symptoms. While various conditions such as diabetes, metabolic disorders, trauma, autoimmune disease, and chemotherapy-induced neurotoxicity have been linked to PN, approximately one-third of PN cases remain idiopathic, underscoring a critical gap in our understanding of these disorders. Over the years, considerable efforts have focused on unraveling the complex molecular pathways underlying PN to advance diagnosis and treatment. Traditional methods such as linkage analysis, fluorescence in situ hybridization, polymerase chain reaction, and Sanger sequencing identified initial genetic variants associated with PN. However, the establishment and application of next-generation sequencing (NGS) and, more recently, long-read/single-cell sequencing have revolutionized the field, accelerating the discovery of novel disease-causing variants and challenging previous assumptions about pathogenicity. This review traces the evolution of genomic technologies in PN research, emphasizing the pivotal role of NGS in uncovering genetic complexities. We provide a comprehensive analysis of established genomic approaches such as genome-wide association studies, targeted gene panel sequencing, and whole-exome/genome sequencing, alongside emerging multiomic technologies including RNA sequencing and proteomics. Integrating these approaches promises holistic insights into PN pathophysiology, potentially revealing new biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Furthermore, we discuss the clinical implications of genomic and multiomic integration, highlighting their potential to enhance diagnostic accuracy, prognostic assessment, and personalized treatment strategies for PN. Challenges and questions in standardizing these technologies for clinical use are raised, underscoring the need for robust guidelines to maximize their clinical utility.
© 2025 The Author(s). Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hanewinckel R., Ikram M. A., and Van Doorn P. A., “Peripheral Neuropathies,” Handbook of Clinical Neurology 138 (2016): 263–282. - PubMed
-
- Castelli G., Desai K. M., and Cantone R. E., “Peripheral Neuropathy: Evaluation and Differential Diagnosis,” American Family Physician 102, no. 12 (2020): 732–739. - PubMed
-
- Rossor A. M., Carr A. S., Devine H., et al., “Peripheral Neuropathy in Complex Inherited Diseases: An Approach to Diagnosis,” Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 88, no. 10 (2017): 846–863. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U19 NS130607/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS135481/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS135481/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- PRG03121/Cerebral Palsy Alliance Research Foundation
- T32GM007067/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS131610/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R25 GM103757/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG000045/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- Dr. Miriam and Sheldon G. Adelson Medical Research Foundation
- T32HG000045/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U19NS130607/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS131610/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH075673/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH075673-011/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS111029/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R25GM103757/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01NS111029/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- Merkin Peripheral Neuropathy and Nerve Regeneration Center
- Hydrocephalus Association
- Washington University School of Medicine
- T32 GM007067/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

