Neural ensembles that encode nocifensive mechanical and heat pain in mouse spinal cord
- PMID: 40128392
- PMCID: PMC12081300
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-025-01921-6
Neural ensembles that encode nocifensive mechanical and heat pain in mouse spinal cord
Abstract
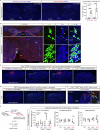
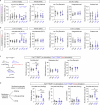
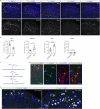
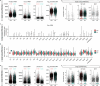
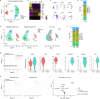
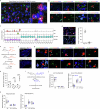
Acute pain is an unpleasant experience caused by noxious stimuli. How the spinal neural circuits attribute differences in quality of noxious information remains unknown. By means of genetic capturing, activity manipulation and single-cell RNA sequencing, we identified distinct neural ensembles in the adult mouse spinal cord encoding mechanical and heat pain. Reactivation or silencing of these ensembles potentiated or stopped, respectively, paw shaking, lifting and licking within but not across the stimuli modalities. Within ensembles, polymodal Gal+ inhibitory neurons with monosynaptic contacts to A-fiber sensory neurons gated pain transmission independent of modality. Peripheral nerve injury led to inferred microglia-driven inflammation and an ensemble transition with decreased recruitment of Gal+ inhibitory neurons and increased excitatory drive. Forced activation of Gal+ neurons reversed hypersensitivity associated with neuropathy. Our results reveal the existence of a spinal representation that forms the neural basis of the discriminative and defensive qualities of acute pain, and these neurons are under the control of a shared feed-forward inhibition.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










References
-
- Bester, H., Chapman, V., Besson, J. M. & Bernard, J. F. Physiological properties of the lamina I spinoparabrachial neurons in the rat. J. Neurophysiol.83, 2239–2259 (2000). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 101053091/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Priority Excellent Science | H2020 European Research Council (H2020 Excellent Science - European Research Council)
- 2019-00761/Vetenskapsrådet (Swedish Research Council)
- 2022-00960/Vetenskapsrådet (Swedish Research Council)
- KAW 2023.0006, KAW 2024.0031/Knut och Alice Wallenbergs Stiftelse (Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

