PIONEER REAL Italy: Real-World Usage of Once-Daily Oral Semaglutide in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 40128506
- PMCID: PMC12006614
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-025-01719-6
PIONEER REAL Italy: Real-World Usage of Once-Daily Oral Semaglutide in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
Introduction: The PIONEER REAL Italy study examined the clinical outcomes associated with oral semaglutide in real-world settings.
Methods: This was a multicenter, prospective, non-interventional, single-arm study in adults with type 2 diabetes (T2D) who were treatment-naive to injectable glucose-lowering medications. Participants initiated oral semaglutide at doses of 3, 7, or 14 mg, and were followed for 34-44 weeks. The primary endpoint was the change in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) from baseline to the end of study (EoS). Secondary endpoints were the change in body weight (BW), the percentage of participants attaining HbA1c < 7%, composite endpoints of HbA1c reduction ≥ 1%-point plus BW reduction (≥ 3%/ ≥ 5%), and treatment satisfaction measured using Diabetes Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaires (DTSQ) status. Safety was assessed in participants who received ≥ 1 dose of oral semaglutide.
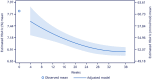
Results: Of 445 eligible participants, 398 completed the study; 351 (78.9%) remained on oral semaglutide at EoS. The median time of treatment follow-up was 40 weeks for each participant. At baseline, participants had a mean (standard deviation [SD]) age of 62.9 (10.2) years, HbA1c of 7.8% (1.3), T2D duration of 8.0 (6.9) years, and BW of 87.8 (19.0) kg. The estimated changes (95% confidence interval) from baseline to EoS in HbA1c and BW were - 0.9%-points (- 1.01 to - 0.82; p < 0.0001) and - 3.8 kg (- 4.45 to - 3.24; p < 0.0001), respectively. At EoS, 65.1% achieved HbA1c < 7%; 25.5% and 19.1% reached HbA1c reduction ≥ 1%-point plus ≥ 3% and ≥ 5% reduction in BW, respectively. DTSQ status improved significantly at EoS (estimated change + 5.24; 95% CI, 5.24 to 6.61, p < 0.0001). Of participants who remained on oral semaglutide at EoS, 72.6% received a 7-mg dose. No new safety signals were observed.
Conclusions: In Italy, the real-world clinical outcomes associated with oral semaglutide in adults with T2D complemented the findings from clinical trials. This reassures oral semaglutide usage in routine clinical practice.
Trial registration: NCT05230615.
Keywords: Body weight; Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist; Glycemic control; Oral semaglutide; Real-world study; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of Interest: Roberta Manti MD has received honorarium and fees for lectures from Novo Nordisk; and has participated in the clinical trials sponsored by Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, and Bayer. Salvatore De Cosmo has received honorarium and fees for lectures from Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Boehringer, AstraZeneca, MSD, Sanofi, Daiichi Sankyo, Bayer, Guidotti. Paolo Desenzani has participated in the clinical trials sponsored by Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, and Sanofi. Lidia Ferrara has participated in the clinical trials sponsored Novo Nordisk. Memoli has received honorarium and fees for lectures from Novo Nordisk, Ely Lilly, AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Bruno Farmaceutici, Abbott, Roche Diagnostics, Novartis and Boehringer, and has participated in the clinical trials sponsored by Novo Nordisk. Angela Girelli has participated in the clinical trials sponsored by Novo Nordisk, Ely Lilly, and Sanofi Pharma. Giuseppe Memoli has received honorarium and fees for lectures Novo Nordisk, Ely Lilly, AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Bruno Farmaceutici, Abbott, Roche diagnostics, Novartis, and Boehringer; and has participated in the clinical trials sponsored by Novo Nordisk. Alessandro Bisio MD is an employee of Novo Nordisk S.p.a, Rome, Italy. Uffe Christian Braae PhD and Alisa Deinega MD, PhD are employees of Novo Nordisk A/S, Søborg, Denmark. Cesare Berra has received honorarium and fees for lectures from Novo Nordisk, Ely Lilly, AstraZeneca, Mundi pharma and Boehringer; and has participated in the clinical trials sponsored by Novo Nordisk Ely Lilly, Sophar and AstraZeneca. Ethical Approval: The study protocol was approved by the appropriate health authorities according to local guidelines and by an Institutional Review Board/Independent Ethics Committee. The study was conducted following Good Pharmacoepidemiology Practices and Good Pharmacovigilance Practices and in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The Ethics Committees included: CET Lombardia 5, Comitato Etico delle Province di Chieti e Pescara, Comitato Etico Catania 1, Comitato Etico Lazio 2, Comitato Etico (CE) Istituti Clinici Scientifici Maugeri, Comitato Etico Casa Sollievo della Sofferenza, CER Umbria, Comitato Etico Palermo 2, Comitato Etico Interaziendale A.O. “SS. Antonio e Biagio e Cesare Arrigo” di Alessandria, Comitato Etico Indipendente Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Consorziale Policlinico di Bari, Comitato Etico Brescia, Comitato Etico Regionale per la Sperimentazione Clinica della Regione Toscana, Comitato Etico Territoriale Interaziendale, Comitato Etico Inter-aziendale Campania Sud, Comitato Etico Campania Nord, Comitato Etico Humanitas, Comitato Etico Azienda Sanitaria Locale Lecce, Comitato Etico per le sperimentazioni cliniche della provincia de Vicenza, Comitato Etico Palermo 1, Comitato Etico di Brescia, Comitato Etico Unico Regionale del Friuli Venezia Giulia, Comitato Etico Campania Centro, Comitato Etico per la Sperimentazione delle Province di Treviso e Belluno. All participants provided written informed consent prior to commencement of any study-related activity. The study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT05230615).
Figures


References
-
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2 Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S17–38. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association. 9 Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(Suppl 1):S111–24. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

