Caregiver burden of Alzheimer's disease among informal caregivers: a cross-sectional study in Malaysia
- PMID: 40128538
- PMCID: PMC11933415
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-95210-8
Caregiver burden of Alzheimer's disease among informal caregivers: a cross-sectional study in Malaysia
Abstract
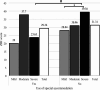
Alzheimer's disease (AD) not only impacts the patients but substantially informal caregivers in terms of physical and psychological burden. This study aims to determine the burden level of informal caregivers of patients with different stages of AD and use of special accommodation (SpA) along with its predictors. A cross-sectional study was conducted by interviewing AD patients and informal caregivers recruited from 4 tertiary hospitals. Zarit Burden Interview (ZBI) was used to estimate caregivers' burden. The analysis categorized informal caregivers of AD patients into two groups based on the use of SpA. Multivariable linear regression was employed to identify potential determinants of subjective caregiver burden. As a result, caregivers' burden experienced by informal caregivers of severe community-dwelling AD patients was significantly higher (p = 0.024) than those with special accommodation. As AD advanced, caregivers' burden was elevated significantly (p = 0.021) from mild to severe AD among community-dwelling patients. In multivariable analysis, severe AD (standardised β = 0.187, p = 0.047 vs. mild AD) and spousal relationship (standardised β = 0.241, p = 0.026 vs. other relationships) were found to be significant factors in predicting caregivers' burden. Hence, the physical and social needs of informal caregivers must not be overlooked. Severe AD significantly increased caregiver burden in community dwelling patients. Spousal caregivers report a higher perceived burden compared to caregivers with other relationships. Policymakers need to recognize and address the substantial demands placed on informal caregivers by providing essential social support. Special accommodation could alleviate the burden on informal caregivers, particularly those caring for patients with severe AD.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical issues: The study obtained ethical approval from the Medical Research and Ethics Committee (NMRR-21-02014-VCP(IIR)). Disclaimers: The views expressed in this publication are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovation (MOSTI), Malaysia.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organisation W. Global action plan on the public health response to dementia 2017–2025. Geneva: World Health Organization. 52. (2017).
-
- Prince, M. J. et al. World Alzheimer Report 2015-The Global Impact of Dementia: An analysis of prevalence, incidence, cost and trends. (2015).
-
- Kawano, Y. et al. Patient affect and caregiver burden in dementia. Psychogeriatrics20 (2), 189–195 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Park, M., Sung, M., Kim, S. K., Kim, S. & Lee, D. Y. Multidimensional determinants of family caregiver burden in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. Psychogeriatr.27 (8), 1355–1364 (2015). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials