Association of Life's Essential 8 with incidence of heart failure modified by depressive symptoms: a prospective cohort study from UK Biobank
- PMID: 40128779
- PMCID: PMC11934694
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-025-04011-3
Association of Life's Essential 8 with incidence of heart failure modified by depressive symptoms: a prospective cohort study from UK Biobank
Abstract
Background: The Life's Essential 8 (LE8) proposed by the American Heart Association for assessing cardiovascular health (CVH) has been demonstrated to be associated with cardiovascular disease, but rarely includes heart failure (HF), and the role of psychological factors has not been considered. We aimed to prospectively investigate the independent, joint, and interactive associations of LE8 and depressive symptoms with HF incidence.
Methods: A total of 336,939 participants recruited from UK Biobank without HF, coronary heart disease, and stroke were included in the cohort study. The LE8 score consisted of four behavioral (diet, physical activity, nicotine exposure, and sleep) and four biological factors (glucose, blood lipids, blood pressure, and body mass index) and was classified into three levels: low, moderate, and high CVH. Depressive symptoms at baseline were identified by self-report and linkage to medical records. Incident HF cases during follow-up were extracted through primary care, hospital admissions, self-reports, and death registrations. Cox proportional hazard models were conducted to examine the associations of LE8 and depressive symptoms with HF incidence, with findings presented as hazard ratios (HRs) (95% confidence interval, CI).
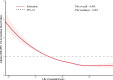
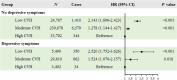
Results: A total of 9379 (2.8%) participants developed HF during a median follow-up of 13.6 years. Compared with low-CVH individuals, the multivariate-adjusted HRs with 95% CI for incident HF were 0.596 (0.565-0.629) and 0.458 (0.408-0.514) in those with moderate and high CVH, respectively. Per standard deviation increment in LE8 was associated with a 25.5% (HR = 0.745; 95% CI: 0.729-0.762) lower risk of HF. The stratification analysis indicated that the detrimental effect of low CVH on HF was more pronounced in participants with depressive symptoms compared to those without, with a significant multiplicative interaction (P for multiplicative interaction = 0.016). The joint test showed that the lowest risk of HF was observed in participants with high CVH and no depressive symptoms (HR = 0.344; 95% CI: 0.295-0.401), which may be attributed to a significant additive interaction observed.
Conclusions: The cohort study revealed that LE8-defined CVH not only could predict the incidence of HF, but also mitigate the increased risk of HF attributable to depressive symptoms. Achieving the high LE8 scores recommended by the AHA to improve CVH will be beneficial in reducing the population burden of HF, especially among patients with depressive symptoms.
Keywords: Cardiovascular health; Depressive symptoms; Incident heart failure; Interaction; Life’s Essential 8.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The Northwest Multi-center Research Ethics Committee (MREC reference: 21/NW/0157) provided ethical approval for the UK Biobank project. All participants gave informed consent before being recruited. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Zhu Z, Li FR, Jia Y, Li Y, Guo D, Chen J, Tian H, Yang J, Yang HH, Chen LH, et al. Association of lifestyle with incidence of heart failure according to metabolic and genetic risk status: a population-based prospective study. Circ Heart Fail. 2022;15(9): e009592. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

