Effects of adenosine triphosphate, thiamine pyrophosphate, melatonin, and liv-52 on subacute pyrazinamide proliferation hepatotoxicity in rats
- PMID: 40128909
- PMCID: PMC11931754
- DOI: 10.1186/s40360-025-00901-7
Effects of adenosine triphosphate, thiamine pyrophosphate, melatonin, and liv-52 on subacute pyrazinamide proliferation hepatotoxicity in rats
Abstract
Background: Hepatotoxicity of pyrazinamide, an antituberculosis drug, limits its therapeutic use and oxidative stress has been implicated in this toxicity. This study investigated the protective effects of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP), melatonin, and Liv-52, which have previously been shown antioxidant activities, on pyrazinamide-induced hepatotoxicity.
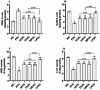
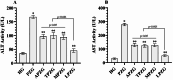
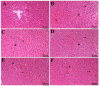
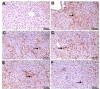
Methods: 36 albino Wistar male rats were divided into randomized six groups; healthy (HG), pyrazinamide (PZG), ATP + pyrazinamide (APZG), TPP + pyrazinamide (TPZG), melatonin + pyrazinamide (MPZG) and Liv-52 + pyrazinamide (LPZG) groups. ATP 4 mg/kg and TPP 25 mg/kg were administered intraperitoneally (IP). Melatonin 10 mg/kg and Liv-52 20 mg/kg were given orally. One hour after administration of ATP, TPP, melatonin, and Liv-52, 250 mg/kg pyrazinamide was applied orally to all rats except HG group. The treatment was repeated (1 × 1) for 4 weeks. Then, blood samples were taken for determination of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) activities. Immediately after, the rats were euthanized with thiopental sodium (50 mg/kg, IP), and the livers were removed. The tissues were analyzed for malondialdehyde (MDA), total glutathione (tGSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT) also hydropic degeneration, necrosis, and apoptosis (caspase 3) were examined.One-Way ANOVA was used in biochemical analyses and Tukey test was used as post-hoc. For histopathological and immunohistochemical analysis, the Kruskal-Wallis test was used and Dunn's test as a post-hoc.
Results: Pyrazinamide increased MDA land decreased tGSH, SOD, and CAT levels in liver tissues (p < 0.001). It also increased serum ALT and AST activities and caused severe hydropic degeneration and necrosis in liver tissue (p < 0.001). ATP, TPP, melatonin, and Liv-52 significantly prevented the biochemical and histopathological changes induced by pyrazinamide (p < 0.05). On the other hand, Liv-52 was more successful than other potential protectors in protecting liver tissue from pyrazinamide damage (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: ATP, TPP, melatonin, and Liv-52 can be used to protect liver tissue from pyrazinamide-induced hepatotoxicity in rats.
Keywords: ATP; Antioxidant effect; Liv-52; Liver toxicity; Pyrazinamide; Thiamine pyrophosphate.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The Erzincan Binali Yıldırım University, local Animal Experimentation Ethics Committee approved the procedures (Date: 29.08.2024, meeting no: 08/31). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

