Monosaccharide-Based Synthetic TLR4 Agonist Enhances Vaccine Efficacy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Challenge
- PMID: 40129118
- PMCID: PMC11998000
- DOI: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.4c00932
Monosaccharide-Based Synthetic TLR4 Agonist Enhances Vaccine Efficacy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Challenge
Abstract
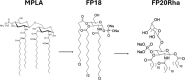
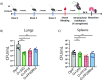
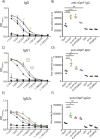
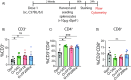
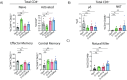
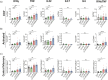
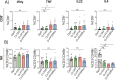
Vaccine adjuvants are critical to improve the immunogenicity, efficacy, and durability of vaccines; however, their development has lagged behind that of vaccine antigens. Monophosphoryl lipid A (MPLA), a clinically approved adjuvant that stimulates Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), faces manufacturing challenges due to its complex and long synthesis. With the aim of simplifying the structure of MPLA while retaining its biological activity, we developed monosaccharide-based molecules FP18 and FP20Rha that activate TLR4 signaling. Both TLR4 agonists induced robust antibody activity against the model antigen, ovalbumin. Here, we report the potential of these TLR4 agonists to enhance the protective efficacy of the well-characterized OprF antigen against P. aeruginosa infection. OprF adjuvanted with FP18 showed reduced bacterial loads in lungs and spleens, relative to antigen alone in an acute P. aeruginosa pneumonia model. FP18-adjuvanted OprF also enhanced the production of anti-OprF antibodies and stimulated IFNγ and TNF in CD4+ T cells, suggesting a Th1-skewed cellular immune response. These adjuvants have promise for accelerating the development of effective vaccines against P. aeruginosa and other infectious diseases.
Keywords: P. aeruginosa; TLR4 agonist; acute pneumonia; infectious diseases; monosaccharide-based adjuvant; vaccine adjuvants; vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PcrV in an intranasal adjuvanted tobacco mosaic virus conjugate vaccine mediates protection from Pseudomonas aeruginosa via an early Th1/Th17 skewed localized and systemic immune response.Vaccine. 2025 Jul 11;60:127306. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2025.127306. Epub 2025 May 26. Vaccine. 2025. PMID: 40424705
-
Intradermal vaccination with a Pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine adjuvanted with a mutant bacterial ADP-ribosylating enterotoxin protects against acute pneumonia.Vaccine. 2019 Feb 4;37(6):808-816. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.12.053. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Vaccine. 2019. PMID: 30638799
-
Mucosal immunization with the lung Lactobacillus-derived amphiphilic exopolysaccharide adjuvanted recombinant vaccine improved protection against P. aeruginosa infection.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Nov 18;20(11):e1012696. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012696. eCollection 2024 Nov. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39556597 Free PMC article.
-
Taking a Toll on human disease: Toll-like receptor 4 agonists as vaccine adjuvants and monotherapeutic agents.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2004 Jul;4(7):1129-38. doi: 10.1517/14712598.4.7.1129. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15268679 Review.
-
Understanding Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Host Interactions: The Ongoing Quest for an Efficacious Vaccine.Cells. 2020 Dec 5;9(12):2617. doi: 10.3390/cells9122617. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33291484 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

