Tracheoesophageal Voicing Following Resistance-Based Dysphagia Rehabilitation: An Exploratory Multidimensional Assessment
- PMID: 40129274
- PMCID: PMC12248270
- DOI: 10.1002/hed.28136
Tracheoesophageal Voicing Following Resistance-Based Dysphagia Rehabilitation: An Exploratory Multidimensional Assessment
Abstract
Background: This exploratory study investigated tracheoesophageal voicing following 6 weeks of resistance-based dysphagia rehabilitation with the SEA2.0, using a multidimensional assessment approach.
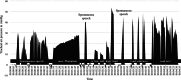
Methods: Twenty laryngectomized participants were assessed at T0 (baseline), T1 (after 6 weeks training), and T2 (after 8 weeks rest). Training included the chin tuck, jaw opening, and effortful swallow against resistance. Multidimensional assessments included acoustic analysis (AVQI, intensity, dynamic range), clinician-rated perceptual evaluations (voice tonicity, intelligibility), PROMs (VHI-10, V-RQOL, CPIB-10), and tracheal manometry and pharyngeal-/esophageal high-resolution impedance manometry during voicing.
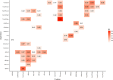
Results: No significant changes in mean AVQI, intensity, dynamic range, voice tonicity, intelligibility, PROMs, and physical outcomes (manometry) were found. However, several clinically relevant changes, mostly improvements, were noted in 14 participants for AVQI and PROMs.
Conclusion: Tracheoesophageal voice, on average, is not affected by resistance-based muscle training for swallowing rehabilitation. For some participants, however, several clinically relevant improvements in voice quality and quality of life were noticeable.
Keywords: high‐resolution (impedance) manometry; swallowing rehabilitation; total laryngectomy; tracheal pressure; tracheoesophageal voice.
© 2025 The Author(s). Head & Neck published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of voice rehabilitation on vocalisation in postlaryngectomy patients: a systematic review.Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2010 Dec;8(4):256-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-1609.2010.00177.x. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2010. PMID: 21091891
-
Long-Term Outcomes of Dysphagia Rehabilitation With an Adjustable Resistance Training Device in Laryngectomized Individuals.Head Neck. 2025 Mar;47(3):801-812. doi: 10.1002/hed.27972. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Head Neck. 2025. PMID: 39440540 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Short- and Longer-Term Effects of Three Intensive Straw Phonation Interventions on the Voice of Female Speech-Language Pathology Students With Mild Dysphonia: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025 Jul-Aug;60(4):e70070. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.70070. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025. PMID: 40622079 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Multidirectional Chin Tuck Against Resistance Exercise on Oropharyngeal Muscles and Swallowing Function in Subacute Stroke Patients With Dysphagia: A Randomised Controlled Trial.J Oral Rehabil. 2025 Jul;52(7):1050-1058. doi: 10.1111/joor.13972. Epub 2025 May 1. J Oral Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 40312765 Clinical Trial.
-
Interventions for dysphagia in long-term, progressive muscle disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Feb 9;2(2):CD004303. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004303.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 26859621 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ackerstaff A. H., Hilgers F. J., Aaronson N. K., and Balm A. J., “Communication, Functional Disorders and Lifestyle Changes After Total Laryngectomy,” Clinical Otolaryngology and Allied Sciences 19, no. 4 (1994): 295–300. - PubMed
-
- Perry A., Casey E., and Cotton S., “Quality of Life After Total Laryngectomy: Functioning, Psychological Well‐Being and Self‐Efficacy,” International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders 50, no. 4 (2015): 467–475. - PubMed
-
- Bickford J., Coveney J., Baker J., and Hersh D., “Living With the Altered Self: A Qualitative Study of Life After Total Laryngectomy,” International Journal of Speech‐Language Pathology 15, no. 3 (2013): 324–333. - PubMed
-
- Hilgers F. J., van Dam F. S., Keyzers S., Koster M. N., van As C. J., and Muller M. J., “Rehabilitation of Olfaction After Laryngectomy by Means of a Nasal Airflow‐Inducing Maneuver: The “Polite Yawning” Technique,” Archives of Otolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery 126, no. 6 (2000): 726–732. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

