Comparison of trend analysis of varicella zoster disease burden between China and the world 1990-2021 and disease burden forecast 2030
- PMID: 40129585
- PMCID: PMC11931152
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1535977
Comparison of trend analysis of varicella zoster disease burden between China and the world 1990-2021 and disease burden forecast 2030
Abstract
Objectives: This study aims to analyze temporal trends in the age- and sex-specific burdens of varicella zoster virus (VZV), including incidence, prevalence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) in China from 1990 to 2021, and to predict the burden of varicella zoster in China for 2030 by comparing the trends with the global burden of the disease.
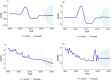
Methods: Data from the Global Burden of Disease database (1990-2021) were used to analyze the characteristics of varicella zoster virus (VZV) burden in China and globally, including trends in incidence, prevalence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs). The average annual percentage change (AAPC) and its corresponding 95% confidence interval (95% CI) were calculated using Joinpoint to assess the VZV burden trends. A comprehensive comparative analysis of the differences in VZV burden between China and the global population was conducted across multiple dimensions, including age, gender, and time period. Additionally, an autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) model was used to predict the VZV trend from 2021 to 2030.
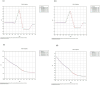
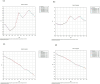
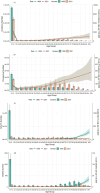
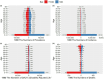
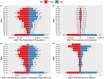
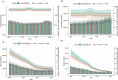
Results: Between 1990 and 2021, the age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR) of varicella zoster in China decreased from 1,274.93/100,000 to 1,270.58/100,000, while the global ASIR increased from 1,244.05/100,000 to 1,248.59/100,000. In China, the age-standardized prevalence rate (ASPR) decreased slightly from 72.27/100,000 to 72.03/100,000, whereas the global ASPR rose from 66.67/100,000 to 67.16/100,000. The age-standardized disability-adjusted life year rate (ASDR) in China decreased significantly, from 17.68/100,000 to 4.66/100,000, while the global ASDR decreased from 19.28/100,000 to 12.31/100,000. Similarly, China's age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) declined significantly, from 0.40/100,000 to 0.05/100,000, while the global ASMR decreased from 0.35/100,000 to 0.19/100,000. Over the same period, the average annual percentage change (AAPC) of ASIR, ASPR, ASMR, and ASDR in China was -0.0056, -0.0131%, -6.84%, and -4.24%, respectively, while the global AAPC for these metrics was 0.0119, 0.0183, -1.97%, and -1.42%, respectively. Additionally, age and gender had a significant impact on the burden of varicella zoster. The trends in ASIR and ASPR were notably influenced by age, while ASMR and ASDR exhibited a significant increasing trend with age. Projections indicate that the ASDR of varicella zoster in China will continue to decrease by 2030, while the ASIR, ASPR, and ASMR are expected to remain stable.
Conclusion: Between 1990 and 2021, the incidence, prevalence, mortality, and DALYs of VZV in China demonstrated a declining trend, reflecting a relative reduction in the VZV burden. Women are more susceptible to VZV infection and face a higher risk of mortality than men. In contrast, the global disease burden remains higher than that in China. Projections suggest a slight decrease in the VZV burden in China by 2030. However, due to the country's large and aging population, VZV will continue to pose a significant public health challenge.
Keywords: disability-adjusted life years; incidence; mortality; prevalence; trend; varicella zoster disease.
Copyright © 2025 Chang, Li, Li, Qin, Hu, Yang, Li and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Burden of uterine cancer in China from 1990 to 2021 and 15-year projection: a systematic analysis and comparison with global levels.Reprod Health. 2024 Oct 10;21(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12978-024-01882-2. Reprod Health. 2024. PMID: 39390595 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal trends of thyroid cancer in China and globally from 1990 to 2021: an analysis of the global burden of Disease Study 2021.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 26;14(1):25538. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77663-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39462100 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of trends in the burden of motor neuron disease in China, the United States, and globally from 1990 to 2021: projections for 2022-2041.Front Neurol. 2025 May 16;16:1539889. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1539889. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40452765 Free PMC article.
-
National and subnational burden of brain and central nervous system cancers in China and global from 1990 to 2021: results from the global burden of disease study 2021.Arch Public Health. 2025 Jul 28;83(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s13690-025-01683-4. Arch Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40722045 Free PMC article.
-
Global and China trends and forecasts of disease burden for female lung Cancer from 1990 to 2021: a study based on the global burden of disease 2021 database.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025 Feb 8;151(2):68. doi: 10.1007/s00432-025-06084-2. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39921760 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xiong S, Han C, Wu D, Mi X, Zhang P, Gao H, et al. . Effectiveness of a 2-dose varicella vaccination program in Changzhou, China, during the transitional period (2017-2022): a registry-based case-cohort study. BMC Public Health. (2025) 25:207. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21348-9, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jejaw M, Tafere TZ, Tiruneh MG, Hagos A, Teshale G, Tilahun MM, et al. . Three in four children age 12-23 months missed opportunities for vaccination in sub-Saharan African countries: a multilevel mixed effect analysis of demographic health and surveys 2016-2023. BMC Public Health. (2025) 25:62. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-21273-3, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

