In-patient expenditure between 2011 and 2021 for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a hospital-based multicenter retrospective study in southwest China
- PMID: 40129587
- PMCID: PMC11931030
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1559424
In-patient expenditure between 2011 and 2021 for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a hospital-based multicenter retrospective study in southwest China
Abstract
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic non-infectious disease that seriously endangers human health. This study aimed to determine the main factors influencing the medical expenditure of T2DM patients and provide guidance for the allocation and control of medical expenditure.
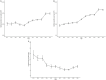
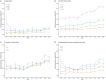
Methods: The homepage data of patients with T2DM were retrospectively collected from six tertiary hospitals in southwest China from January 2011 to December 2021. A multiple linear regression model was constructed to examine the factors associated with medical expenses per patient. Furthermore, the trends of medical expenditure according to other important measures and patient subgroups were described, and a proportional breakdown of medical expenditure was generated. All expenditure data were reported in Chinese Yuan (CNY), based on the 2021 value, and adjusted using the year-specific healthcare consumer price index.
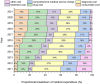
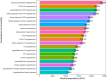
Results: A total of 45,237 patients with T2DM were analyzed in this study. Multiple linear regression showed that age, marital status, insurance type, length of stay, number of clinical visits, number of comorbidities, history of disease, history of surgery, smoking history, and the age-adjusted Charlson comorbidity index score were influencing factors of medical expenditure in patients with T2DM. Considering the overall average medical expenditure, diagnosis cost accounted for the largest proportion and was never <25% since 2011, showing a decreasing trend year by year. Among the types of comorbidity, hypertension was the most prevalent, followed by kidney disease and hyperlipidemia. In terms of the combination of comorbidities, medical expenditure was the highest for pulmonary infection+hypertension (24,360 CNY), followed by coronary heart disease+heart failure+hypertension (22,029 CNY).
Conclusions: Identifying the main factors influencing the medical expenditure of patients with T2DM can provide a reference for the medical security department to formulate reasonable compensation plans and for medical institutions to optimize treatment plans. Ultimately, this might reduce the financial burden of patients and relieve the pressure of medical insurance funds.
Keywords: influencing factors; medical expenditure; multiple linear regression; time trend; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2025 He, Tan, Tan, Zhang, Liu and Tang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for diabetes: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2010 Feb;14(11):iii-iv, xi-xvi, 1-181. doi: 10.3310/hta14110. Health Technol Assess. 2010. PMID: 20223123
-
Diet, physical activity or both for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in people at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 4;12(12):CD003054. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003054.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29205264 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapy for Gaucher's disease: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Jul;10(24):iii-iv, ix-136. doi: 10.3310/hta10240. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16796930
-
What is the value of routinely testing full blood count, electrolytes and urea, and pulmonary function tests before elective surgery in patients with no apparent clinical indication and in subgroups of patients with common comorbidities: a systematic review of the clinical and cost-effective literature.Health Technol Assess. 2012 Dec;16(50):i-xvi, 1-159. doi: 10.3310/hta16500. Health Technol Assess. 2012. PMID: 23302507 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, et al. . Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2019) 157:107843. 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

