The association between oxidative balance score and gallstones in adults: a population-based study
- PMID: 40129666
- PMCID: PMC11932657
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1534336
The association between oxidative balance score and gallstones in adults: a population-based study
Abstract
Purpose: Oxidative stress is a significant contributor to the progression of gallstones. However, the combined or independent effects of dietary and lifestyle pro-antioxidants and antioxidants on gallstone formation remain unclear. Our study aims to investigate the potential link between the oxidative balance score (OBS) and the occurrence of gallstones.
Patients and methods: This study utilized data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), conducted in the United States between 2017 and March 2020, identifying 750 gallstone cases among the 7,489 participants. Gallstone status was self-reported. The data in this study were analyzed using a range of statistical techniques, such as Multivariable logistic regression, restricted cubic spline curves (RCS), mediation effects analysis, subgroup analyses and sensitivity analysis.
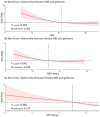
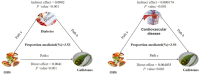
Results: Using fully adjusted multivariable logistic regression analysis, we identified a significant negative correlation between OBS and the occurrence of gallstones, with an odds ratio (OR) of 0.97 and a 95% confidence interval (CI) of 0.96 to 0.99. Furthermore, participants in the highest quartile of OBS exhibited a 41% reduced risk of gallstones compared to those in the lowest quartile, with an OR of 0.59 (95% CI: 0.45, 0.79) relative to the reference population. Additionally, a linear inverse association between OBS and gallstones was observed. Mediation analysis indicated that diabetes and cardiovascular diseases (CVD) mediated 3.5 and 4% of the association between OBS and gallstones, respectively.
Conclusion: This research suggests that lower OBS levels are associated with a higher susceptibility to gallstone formation, potentially offering a new perspective on clinical strategies for the management and prevention of gallstones.
Keywords: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; cross-sectional study; diabetes mellitus; gallstones; mediation analyses; oxidative balance score.
Copyright © 2025 Yang, Wang, Liu, Yu, Chen and Du.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Higher levels of oxidative balance score linked to lower risk of gallstones: findings from the 2017-2020 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.Front Nutr. 2025 Jan 29;12:1521882. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1521882. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39944962 Free PMC article.
-
Association between oxidative balance score and gallstone disease: a population-based study from NHANES.Front Nutr. 2025 Jan 22;12:1539969. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1539969. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39911802 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative balance scores and gallstone disease: mediating effects of oxidative stress.Nutr J. 2025 Jan 10;24(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12937-025-01073-0. Nutr J. 2025. PMID: 39789597 Free PMC article.
-
Association of oxidative balance score with hyperuricemia and gout: NHANES 2009-2018.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Nov 4;15:1402369. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1402369. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39558977 Free PMC article.
-
Association between chronic kidney disease and oxidative balance score: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2005-2018.Front Nutr. 2025 Jan 3;11:1406780. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1406780. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39830066 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

