AQP1 Affects Necroptosis by Targeting RIPK1 in Endothelial Cells of Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 40129682
- PMCID: PMC11932119
- DOI: 10.2147/VHRM.S487327
AQP1 Affects Necroptosis by Targeting RIPK1 in Endothelial Cells of Atherosclerosis
Abstract
Purpose: Aquaporin 1 (AQP1), a transmembrane water channel protein, has been implicated in the regulation of necroptosis. However, its specific role in atherosclerotic plaque stability through the modulation of necroptosis remains unclear. Therefore, in this study, we aim to investigate whether AQP1 influences necroptosis in atherosclerosis by binding to receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) and decreasing the expression of receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 (RIPK3) and mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase (MLKL).
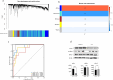
Patients and methods: The gene expression of AQP1 and necroptosis-associated genes significantly differ between atherosclerosis and normal groups. Genes linked to necroptosis were screened to influence the AS identified by weighted gene coexpression network analysis (WGCNA). Then we collected femoral atherosclerosis and normal aortic samples, further conducted single-cell sequencing and spatial transcriptomic methods to confirm the potential function and pathway of AQP1 in endothelial cells. Meanwhile, we overexpressed AQP1 in ox-LDL-treated endothelial cells in vitro.
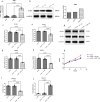
Results: Firstly, via single-sample Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (ssGSEA) scores, we found that necroptosis plays the most important role among all ways of programmed cell death in two kinds of atherosclerosis. AQP1, RIPK1, RIPK3 and MLKL express differently in normal and atherosclerosis tissue by differentially expressed gene (DEG) analysis and Western Blot (WB). WGCNA analysis indicates that AQP1, MLKL and RIPK3 were significantly related to the AS. The area under the curve of the above hub genes was greater than 0.8 (AQP1 0.946, RIPK1 0.908, RIPK3 0.988, MLKL 0.863). We found AQP1 highly enriched in endothelial cells (ECs) by single-cell analysis. We sequenced the samples by spatial transcriptome and found that AQP1 was also mainly enriched in ECs both in expression and spatial location. With AQP1 overexpression in ECs, it significantly inhibited the expression of MLKL and RIPK3 and stimulated EC proliferation.
Conclusion: Our study identified that AQP1 suppresses atherosclerotic necroptosis by inhibiting the expression of RIPK3 and MLKL in ECs which might indicates that AQP1 plays a role in atherosclerosis. This new mechanism contributes to improving the diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic outcomes of atherosclerosis.
Keywords: carotid atherosclerosis; mechanism; necroptosis; plaque.
© 2025 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





References
-
- Kluck GEG, Qian AS, Sakarya EH, Quach H, Deng YD, Trigatti BL. Apolipoprotein A1 protects against necrotic core development in atherosclerotic plaques: PDZK1-dependent high-density lipoprotein suppression of necroptosis in macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2023;43:45–63. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.122.318062 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

