A rare clinical presentation of metronidazole-induced dysarthria: A Case report with literature review
- PMID: 40129781
- PMCID: PMC11930524
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2025.02.042
A rare clinical presentation of metronidazole-induced dysarthria: A Case report with literature review
Abstract
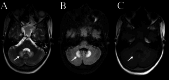
We described a case of a rare, but notable adverse effect of metronidazole therapy, where a 55-year-old chronic alcoholic patient developed dysarthria following a four-week course of the drug for the treatment of pyogenic liver abscesses. Dysarthria, characterized by slurred or unclear speech, is an uncommon complication of metronidazole, which is generally well-tolerated but has the potential to cause neurotoxic effects in some individuals, especially with prolonged use or high cumulative doses. In this case, the Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) brain revealed T2/FLAIR hyperintensities involving the bilateral dentate nuclei, a key finding associated with metronidazole-induced encephalopathy. The exclusion of other possible causes for dysarthria led to the conclusion that the symptoms were likely induced by metronidazole. This highlights the importance of considering drug-induced neurotoxicity in patients presenting with new neurological symptoms, particularly when there is a history of prolonged antibiotic therapy. The patient's improvement after discontinuing metronidazole and switching to alternative treatment further supports this diagnosis. This case underscores the necessity of closely monitoring patients on metronidazole, especially those receiving prolonged treatment, for any emerging neurological signs. Typical MRI findings play a crucial role in the vigilance for the diagnosis and treatment of such clinical situations. Timely recognition and intervention can help prevent permanent damage and facilitate recovery.
Keywords: Antibiotic; Central nervous system; Cerebellum; Dysarthria; Encephalopathy; Liver abscess; Metronidazole.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of University of Washington.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A case of methylprednisolone treatment for metronidazole-induced encephalopathy.BMC Neurol. 2019 Mar 30;19(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12883-019-1278-6. BMC Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30927916 Free PMC article.
-
Metronidazole-Induced Encephalopathy in Alcoholic Liver Disease: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenge.J Emerg Med. 2016 Oct;51(4):e79-e83. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2016.05.038. Epub 2016 Jul 25. J Emerg Med. 2016. PMID: 27471133
-
[A case of metronidazole-induced encephalopathy that is difficult to differentiate from Wernicke encephalopathy].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2024 Sep 26;64(9):637-641. doi: 10.5692/clinicalneurol.cn-001972. Epub 2024 Aug 24. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2024. PMID: 39183051 Japanese.
-
[Clinical Characteristics of Metronidazole-induced Encephalopathy: A Report of Two Cases and a Review of 32 Japanese Cases in the Literature].Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 2015 Sep;89(5):559-66. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi.89.559. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 2015. PMID: 26630786 Review. Japanese.
-
Metronidazole-induced encephalopathy: a systematic review.J Neurol. 2020 Jan;267(1):1-13. doi: 10.1007/s00415-018-9147-6. Epub 2018 Dec 7. J Neurol. 2020. PMID: 30536109
Cited by
-
Letter to the editor regarding: "A rare clinical presentation of metronidazole-induced dysarthria: A Case report with literature review".Radiol Case Rep. 2025 Jul 5;20(9):4835-4836. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2025.06.025. eCollection 2025 Sep. Radiol Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40686807 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

