A comprehensive review of methodologies and application to use the real-world data and analytics platform TriNetX
- PMID: 40129946
- PMCID: PMC11931024
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1516126
A comprehensive review of methodologies and application to use the real-world data and analytics platform TriNetX
Abstract
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are the gold standard for evaluating the efficacy and safety of both pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions. However, while they are designed to control confounders and ensure internal validity, their usually stringent inclusion and exclusion criteria often limit the generalizability of findings to broader patient populations. Moreover, RCTs are resource-intensive, frequently underpowered to detect rare adverse events, and sometimes narrowly focused due to their highly controlled environments. In contrast, real-world data (RWD), typically derived from electronic health records (EHRs) and claims databases, offers a valuable counterpart for answering research questions that may be impractical to address through RCTs. Recognizing this, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has increasingly relied on real-world evidence (RWE) from RWD to support regulatory decisions and post-market surveillance. Platforms like TriNetX, that leverage large-scale RWD, facilitate collaborations between academia, industry, and healthcare organizations, and constitute an in-depth tool for retrieval and analysis of RWD. TriNetX's federated network architecture allows real-time, privacy-compliant data access, significantly enhancing the ability to conduct retrospective studies and refine clinical trial designs. With access to currently over 150 million EHRs, TriNetX has proven particularly effective in filling gaps left by RCTs, especially in the context of rare diseases, rare endpoints, and diverse patient populations. As the role of RWD in healthcare continues to expand, TriNetX stands out as a critical tool that complements traditional clinical trials, bridging the gap between controlled research environments and real-world practice. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of the methodologies and applications of the TriNetX platform, highlighting its potential contribution to advance patient care and outcomes.
Keywords: Kaplan–Meier estimator; TriNetX; cohort study; drug discovery; real-world data.
Copyright © 2025 Ludwig, Anson, Zirpel, Thaci, Olbrich, Bieber, Kridin, Dempfle, Curman, Zhao and Alam.
Conflict of interest statement
HZ has received financial support for attending meetings and/or travel from Pfizer, UCB Pharma, Almirall, Janssen, and TriNetX. HO has received financial support to attend meetings from TriNetX. RL has received honoraria for speaking or consulting or has obtained research grants from Novartis, Lilly, Bayer, Dompe, Synthon, Argen-X, Pharmaxis, CSL, TriNetX and Monasterium Laboratories during the last 3 years. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

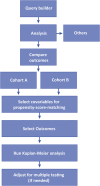


References
-
- Anson M., Henney A. E., Broadwell N., Zhao S. S., Ibarburu G. H., Lip G. Y. H., et al. (2024b). Incidence of new onset type 2 diabetes in adults living with obesity treated with tirzepatide or semaglutide: real world evidence from an international retrospective cohort study. eClinicalMedicine 75, 102777. 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102777 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anson M., Malik A., Zhao S. S., Austin P., Ibarburu G. H., Jaffar S., et al. (2024a). Treating type 2 diabetes with early, intensive, multimodal pharmacotherapy: real‐world evidence from an international collaborative database. J. Diabetes Res. 2024, 3470654. 10.1155/2024/3470654 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

