Interleukin-27-polarized HIV-resistant M2 macrophages are a novel subtype of macrophages that express distinct antiviral gene profiles in individual cells: implication for the antiviral effect via different mechanisms in the individual cell-dependent manner
- PMID: 40129989
- PMCID: PMC11931227
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1550699
Interleukin-27-polarized HIV-resistant M2 macrophages are a novel subtype of macrophages that express distinct antiviral gene profiles in individual cells: implication for the antiviral effect via different mechanisms in the individual cell-dependent manner
Abstract
Introduction: Interleukin (IL)-27 is an anti-viral cytokine. IL-27-treated monocyte-derived macrophages (27-Mac) suppressed HIV replication. Macrophages are generally divided into two subtypes, M1 and M2 macrophages. M2 macrophages can be polarized into M2a, M2b, M2c, and M2d by various stimuli. IL-6 and adenosine induce M2d macrophages. Since IL-27 is a member of the IL-6 family of cytokines, 27-Mac was considered M2d macrophages. In the current study, we compared biological function and gene expression profiles between 27-Mac and M2d subtypes.
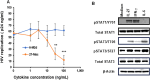
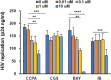
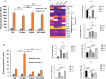
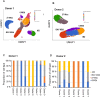
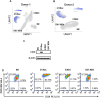
Methods: Monocytes derived from health donors were differentiated to M2 using macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Then, the resulting M2 was polarized into different subtypes using IL-27, IL-6, or BAY60-658 (an adenosine analog). HIV replication was monitored using a p24 antigen capture assay, and the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) was determined using a Hydrogen Peroxide Assay. Phagocytosis assay was run using GFP-labeled opsonized E. coli. Cytokine production was detected by the IsoPlexis system, and the gene expression profiles were analyzed using single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq).
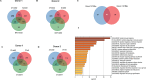
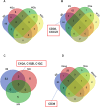
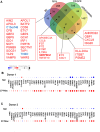
Results and discussion: 27-Mac and BAY60-658-polarized M2d (BAY-M2d) resisted HIV infection, but IL-6-polarized M2d (6-M2d) lacked the anti-viral effect. Although phagocytosis activity was comparable among the three macrophages, only 27-Mac, but neither 6-M2d nor BAY-M2d, enhanced the generation of ROS. The cytokine-producing profile of 27-Mac did not resemble that of the two subtypes. The scRNA-seq revealed that 27-Mac exhibited a different clustering pattern compared to other M2ds, and each 27-Mac expressed a distinct combination of anti-viral genes. Furthermore, 27-Mac did not express the biomarkers of M2a, M2b, and M2c. However, it significantly expressed CD38 (p<0.01) and secreted CXCL9 (p<0.001), which are biomarkers of M1.
Conclusions: These data suggest that 27-Mac may be classified as either an M1-like subtype or a novel subset of M2, which resists HIV infection mediated by a different mechanism in individual cells using different anti-viral gene products. Our results provide a new insight into the function of IL-27 and macrophages.
Keywords: M2 macrophages; anti-viral genes; interleukin-27; polarization; scRNA seq.
Copyright © 2025 Imamichi, Yang, Chen, Goswami, Marquez, Kariyawasam, Sharma, Wiscovitch-Russo, Li, Aioi, Adelsberger, Chang, Higgins and Sui.
Conflict of interest statement
Author AA was employed by the company Septem-Soken. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Polarized Tissue-Derived Macrophages Display Enhanced M2d Phenotype after Prolonged Stimulation with Adenosine A2A Receptor Agonist in the Presence of LPS.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2025 Feb 17;30(2):27638. doi: 10.31083/FBL27638. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2025. PMID: 40018944
-
Transcriptome analysis of IL-10-stimulated (M2c) macrophages by next-generation sequencing.Immunobiology. 2017 Jul;222(7):847-856. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2017.02.006. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Immunobiology. 2017. PMID: 28318799 Free PMC article.
-
IL-27, a novel anti-HIV cytokine, activates multiple interferon-inducible genes in macrophages.AIDS. 2008 Jan 2;22(1):39-45. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3282f3356c. AIDS. 2008. PMID: 18090390
-
Regulation of Macrophage Polarization and Wound Healing.Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2012 Feb;1(1):10-16. doi: 10.1089/wound.2011.0307. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2012. PMID: 24527272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage polarization and HIV-1 infection.J Leukoc Biol. 2010 Apr;87(4):599-608. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1009673. Epub 2009 Dec 30. J Leukoc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20042468 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

