IFN-γ and donor leukocyte infusions for relapsed myeloblastic malignancies after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- PMID: 40131369
- PMCID: PMC12128990
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.190655
IFN-γ and donor leukocyte infusions for relapsed myeloblastic malignancies after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Abstract
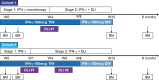
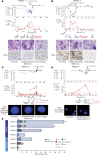
BACKGROUNDThe graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) effect contributes to the efficacy of allogeneic stem cell transplantation (alloSCT). However, relapse, indicative of GVL failure, is the greatest single cause of treatment failure. Based on preclinical data showing that IFN-γ is important to sensitize myeloblasts to alloreactive T cells, we performed a phase I trial of IFN-γ combined with donor leukocyte infusions (DLIs) in myeloblastic malignancies that relapsed after HLA-matched alloSCT.METHODSPatients with relapsed acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome after alloSCT were eligible. Patients self-administered IFN-γ for 4 weeks (cohort 1) or 1 week (cohort 2), followed by DLI and concurrent IFN-γ for a total of 12 weeks. Bone marrow samples were analyzed by single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-Seq) to assess in vivo responses to IFN-γ by malignant myeloblasts.RESULTSIFN-γ monotherapy was well tolerated by all participants (n = 7). Treatment-related toxicities after DLI included grade I-II graft-versus-host disease (n = 5), immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (n = 2), and idiopathic pulmonary syndrome (n = 1), all of which resolved with corticosteroids. Four of 6 DLI recipients achieved minimal residual disease-negative complete remissions and full donor hematopoietic recovery. Median overall survival was 579 days (range, 97-906) in responders. scRNA-Seq validated in vivo activation of the IFN-γ response pathway in hematopoietic stem cell-like or myeloid progenitor cells after IFN-γ in analyzed samples.CONCLUSIONIFN-γ was safe and well tolerated in this phase I study of IFN-γ for relapsed acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome after alloSCT, with a promising efficacy signal when combined with DLI. Larger studies are needed to formally test the efficacy of this approach.TRIAL REGISTRATIONClinicalTrials.gov NCT04628338.FUNDINGUPMC Hillman Cancer Center Cancer Immunology and Immunotherapy Program Pilot Award and Cure Within Reach: Drug Repurposing Clinical Trials to Impact Blood Cancers.
Keywords: Cancer; Cytokines; Hematology; Immunotherapy; Transplantation.
Figures



References
-
- Alyea EP, et al. NCI First International Workshop on The Biology, Prevention and Treatment of Relapse after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: report from the committee on prevention of relapse following allogeneic cell transplantation for hematologic malignancies. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010;16(8):1037–1069. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2010.05.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bishop MR, et al. Introduction to the reports from the National Cancer Institute First International Workshop on the Biology, Prevention, and Treatment of Relapse after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010;16(5):563–564. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2010.02.025. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wayne AS, et al. Proceedings from the National Cancer Institute’s Second International Workshop on the Biology, Prevention, and Treatment of Relapse after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: introduction. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013;19(11):1534–1536. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2013.08.016. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

