Seroprevalence and risk factors of hepatitis B virus infection among healthcare workers in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40131963
- PMCID: PMC11936272
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319986
Seroprevalence and risk factors of hepatitis B virus infection among healthcare workers in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Healthcare workers are at an increased risk of hepatitis B virus infection due to potential exposure to blood and other infectious materials. The infection can lead to acute liver disease and chronic liver complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer. It can impact workforce health, leading to absenteeism, and increased healthcare costs. Hence, this study aimed to determine the seroprevalence and risk factors of the hepatitis B virus among healthcare workers in Africa.
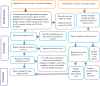
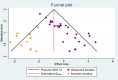
Materials and methods: The protocol for this systematic review and meta-analysis was registered on PROSPERO with the registration number CRD42024556654. Literatures were searched from PubMed, Science Direct, HINARI, African Online Journal, Google Scholar, Google, Semantic Scholar, and Directory of Open Access Journals using relevant search terms. The process of searching relevant articles was completed on 1 August 2024. Studies with a quality evaluation indicator score of 50% or above were included in this study. The random effect model was used to measure the pooled seroprevalence and associated factors of hepatitis B virus infection among healthcare workers in Africa. The finding of the meta-analysis was presented using forest plots with a 95% confidence interval.
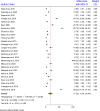
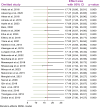
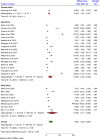
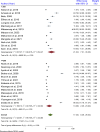
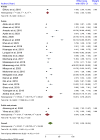
Result: Among 26 studies selected for meta-analysis, 6983 participants were included. The inclusion of 26 studies showed that the pooled prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection among healthcare workers was 17.2% (95% CI: 8.36, 26.04). Healthcare workers diagnosed with liver disease were 5.01 times more likely to having hepatitis B virus infection compared to those who were not diagnosed (POR = 5.01: 95% CI; 2.25,7.77). In addition, healthcare workers who did not receive technical training were 2.70 times more likely to having HBV infection than those who received training (POR = 2.70:95% CI; 1.10, 4.30). Furthermore, healthcare workers aged 40 years and above were 2.53 times more likely to having hepatitis B virus infection than young healthcare workers (POR = 2.53: 95% CI; 1.29,3.77).
Conclusion: The pooled prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection was high. Previously diagnosed liver diseases, the absence of technical training, and the age of healthcare workers were the factors influencing the pooled prevalence of HBV infection among healthcare workers. Hence, providing appropriate medical follow-up for healthcare workers diagnosed with liver disease, comprehensive training and education, and early detection and diagnosis of healthcare workers aged 40 years and above are the most important interventions to prevent the risk of hepatitis B virus infection.
Copyright: © 2025 Berhanu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing of interests.
Figures


References
-
- WHO. Global hepatitis report: Action for access in low- and middle-income countries. 2024. [cited 2024 July 29]. Available from: Global hepatitis report 2024: action for access in low- and middle-incom...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

