A predictive machine learning model for cannabinoid effect based on image detection of reactive oxygen species in microglia
- PMID: 40131976
- PMCID: PMC11936260
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320219
A predictive machine learning model for cannabinoid effect based on image detection of reactive oxygen species in microglia
Abstract
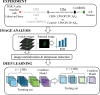
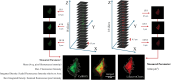
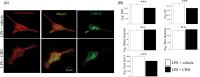
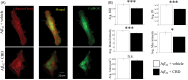
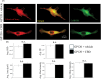
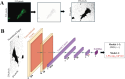
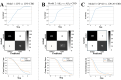
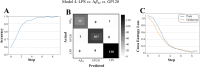
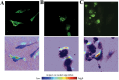
Neuroinflammation is a key feature of human neurodisease including neuropathy and neurodegenerative disease and is driven by the activation microglia, immune cells of the nervous system. During activation microglia release pro-inflammatory cytokines as well as reactive oxygen species (ROS) that can drive local neuronal and glial damage. Phytocannabinoids are an important class of naturally occurring compounds found in the cannabis plant (Cannabis sativa) that interact with the body's endocannabinoid receptor system. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a prototype phytocannabinoid with anti-inflammatory properties observed in cells and animal models. We measured ROS in human microglia (HMC3) cells using CellROX, a fluorescent dynamic ROS indicator. We tested the effect of CBD on ROS level in the presence of three known immune activators: lipopolysaccharide (LPS), amyloid beta (Aβ42), and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) glycoprotein (GP120). Confocal microscopy images within microglia were coupled to a deep learning model using a convolutional neural network (CNN) to predict ROS responses. Our study demonstrates a deep learning platform that can be used in the assessment of CBD effect in immune cells using ROS image measure.
Copyright: © 2025 Sinclair et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Romero-Zerbo SY, García-Fernández M, Espinosa-Jiménez V, Pozo-Morales M, Escamilla-Sánchez A, Sánchez-Salido L, et al.. The atypical cannabinoid abn-cbd reduces inflammation and protects liver, pancreas, and adipose tissue in a mouse model of prediabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:103. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00103 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

