Performance of quantitative point-of-care tests to measure G6PD activity: An individual participant data meta-analysis
- PMID: 40132008
- PMCID: PMC11936200
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012864
Performance of quantitative point-of-care tests to measure G6PD activity: An individual participant data meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency is the main risk factor for severe haemolysis following treatment with 8-aminoquinolines (8AQ). The World Health Organization recommends G6PD testing prior to 8AQ-based hypnozoitocidal treatment.
Methods: We undertook an individual level meta-analysis of the performance of commercially available quantitative point-of-care diagnostics (PoCs) compared with reference spectrophotometry. A systematic literature search (PROSPERO: CRD42022330733) identified 595 articles of which 16 (2.7%) fulfilled pre-defined inclusion criteria and were included in the analysis, plus an additional 4 datasets. In total there were 12,678 paired measurements analyzed, 10,446 (82.4%) by STANDARD G6PD Test (SD Biosensor, RoK, [SDB]), 2,042 (16.1%) by CareStart G6PD Biosensor (AccessBio, USA, [CSA]), 150 (1.2%) by CareStart Biosensor (WellsBio, RoK [CSW]), and 40 (0.3%) by FINDER (Baebies, USA, [FBA]).
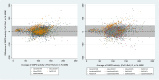
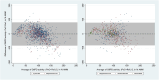
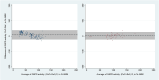
Findings: The pooled sensitivities of the SDB when measuring G6PD activity <30% of normal were 0.82 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.72-0.89) for capillary and 0.93 (95% CI: 0.75-0.99) for venous blood samples. The corresponding values for measuring <70% G6PD activity were 0.93 (95% CI: 0.67-0.99) and 0.89 (95% CI: 0.73-0.96), respectively. The pooled specificity of the SDB was high (>96%) for all blood samples and G6PD activity thresholds. Irrespective of the blood samples and thresholds applied, sensitivity of the CSA did not exceed 62%, although specificity remained high at both 30% and 70% thresholds (>88%). Only one study each for CSW and FBA was included. Sensitivities of the CSW were 0.04 (95% CI: 0.01-0.14) and 0.81 (95% CI: 0.71-0.89) at the 30% and 70% thresholds, respectively (venous blood samples). Sensitivities of the FBA were 1.00 (95% CI: 0.29-1.00) and 0.75 (95% CI: 0.19-0.99) at the 30% and 70% thresholds (venous blood samples). Specificities of the CSW and FBA were consistently high (>90%) at both thresholds. Accuracy of the SDB was higher in females at the 30% cut-off (OR: 3.49, p=0.002) and lower in malaria patients at the 70% cut-off (OR: 0.59, p = 0.005).
Conclusions: The SDB performed better than other PoCs. More evidence was available for the performance of the SDB compared to other PoCs, giving higher confidence in its utility in diagnosing G6PD deficiency.
Copyright: © 2025 Sadhewa et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Edgcomb J, Arnold J, Yount E, Alving A, Eichelberger L, Jeffery G. Primaquine, SN 13272, a new curative agent in vivax malaria; a preliminary report. Journal National Malaria Society (US). 1950;9(4):285–92. - PubMed
-
- von Seidlein L, Auburn S, Espino F, Shanks D, Cheng Q, McCarthy J, et al. Review of key knowledge gaps in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency detection with regard to the safe clinical deployment of 8-aminoquinoline treatment regimens: a workshop report. Malar J. 2013;12:112. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-12-112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

